Dns lookup failed что значит
Dns name lookup failure
Невозможно представить своё существование без доступа к источникам информации, который даёт интернет. Связующим звеном сети компьютеров являются DNS серверы. К сожалению, иногда в их работе возникают ошибки. В этих случаях доступ к интернету ограничен или его нет совсем. Поэтому каждому пользователю не помешают базовые знания по теме.
Что такое DNS сервер, почему могут возникать ошибки
Если объяснять простыми словами, можно назвать DNS сервер адресной книгой интернета. Каждый подключённый к сети компьютер получает идентификатор IP — адрес в виде цифрового значения подобного к такому — 127.0.0.1. Каждый опубликованный сайт имеет доменное имя — http://hostus.ru. Основная задача DNS сервера — преобразование (трансляция) доменного имени в IP адреса и обратный процесс.
Видео: объяснение принципов работы DNS сервера
К сожалению, иногда в цепочке происходят сбои. Возникают ошибки. Причин может быть довольно много, рассмотрим самые распространённые:
Устранение неполадок нужно начинать, проверяя простейшие настройки, и только в случае неудачи осторожно переходить к более сложным действиям.
Общие ошибки DNS
Рассмотрим самые распространённые ошибки, которые обычно легко устранить собственными силами. Как правило, исправление не занимает слишком много времени.
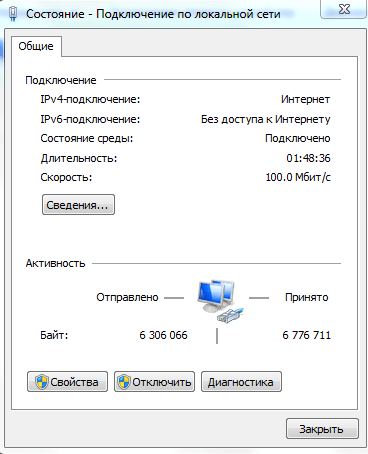
DNS сервер не отвечает, не удаётся найти DNS адрес сервера
Наверное, наиболее часто встречающаяся проблема.
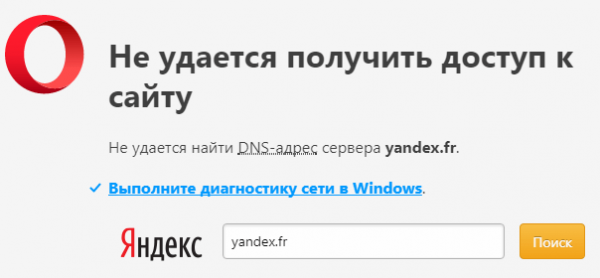
Так выглядит сообщение об ошибке в окне браузера
Когда ошибка появляется в результате попытки входа на определённый ресурс, а остальные прекрасно работают, вероятней всего, проблемы возникают на сайте. Что-то исправить в этом случае не получится. Наберитесь терпения, возможно, через время всё будет работать в штатном порядке.
Ошибки DNS могут появляться по причине неисправностей в работе роутера. А также в их возникновении может быть виноват интернет-провайдер. Перезагрузите или выключите на время маршрутизатор, возможно, это действие уберёт ошибку. Изменений нет — попытайтесь подключить интернет-кабель к ПК или ноутбуку напрямую, минуя роутер. Если действие не помогло, звоните своему провайдеру, вероятно, проблема на его стороне.
Когда все устройства работают нормально, а ошибка возникает на одном компьютере, скорее всего, она связана с неправильной работой самого устройства. Рассмотрение подобной ошибки достойно отдельной публикации.
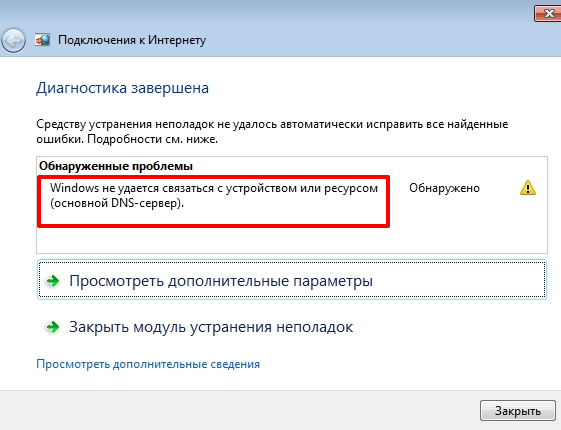
Windows не удаётся связаться с устройством или ресурсом
Рассмотрим такой вариант — основные приложения продолжают работать, интернет подключён, но нужный нам ресурс недоступен, при обращении к сайту на экране появляется сообщение: «Не удаётся найти DNS адрес сервера».
Браузер выдает сообщение об ошибке
Для выяснения причин ошибки проведите диагностику сети:
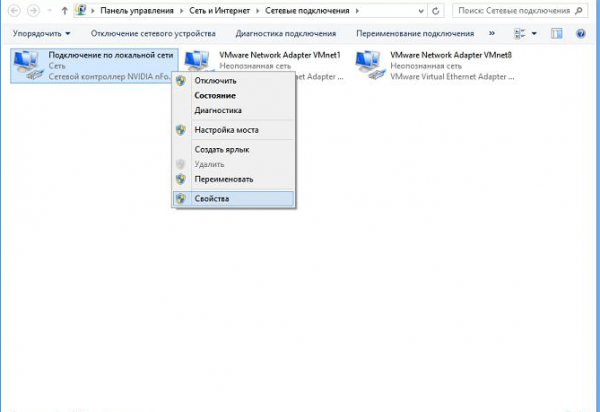
- Для этого правой кнопкой мыши нажмите значок сетевых подключений в нижней части экрана.
Для проведения диагностики сети нажмите значок правой кнопкой мыши
Сообщение о неудаче при попытке системы подключиться к DNS серверу
У этой ошибки могут быть разные причины возникновения. Методы решения проблемы подбираются соответственно:
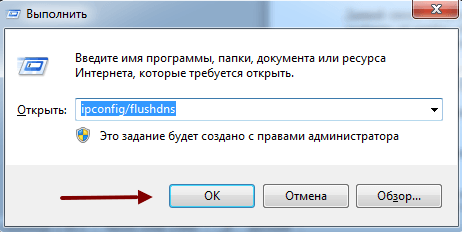
Если все перечисленные действия не увенчались успехом попытайтесь сбросить DNS кэш. Нажмите Win+R, в появившемся окне наберите «ipconfig/flushdns», запустите процесс.
DNS кэш чистится запуском команды «ipconfig/flushdns»
После выполненных действий все должно работать нормально.
Нет доступа к DNS серверу
Пользователи часто встречаются с ситуацией, когда все устройства работают нормально, оплата провайдеру перечислена, но доступ к Всемирной паутине отсутствует. Причина ошибки — некорректные настройки доступа к интернету. Все можно исправить собственными силами.
Для устранения возникшей ошибки произведите такие действия:
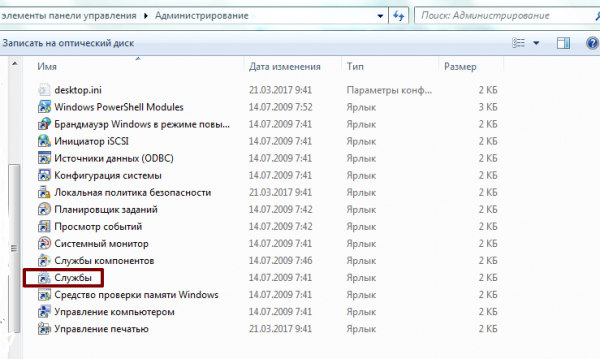
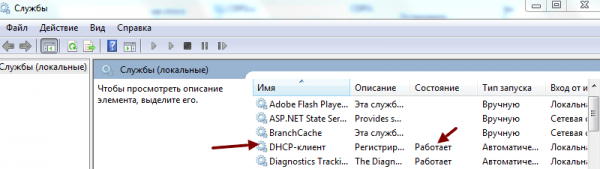
- В меню «Пуск», войдите в «Панель управления», пункт — «Администрирование», выберите раздел — «Службы».
Выбираете пункт службы раздела администрирование, панели управления Windows
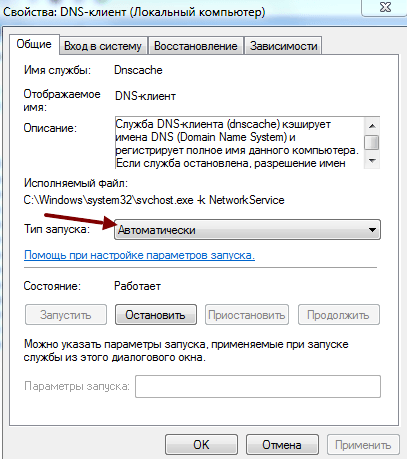
При работающем DNS в строке DNSP-клиент всегда есть запись «Работает»
На вкладке необходимо указать тип запуска: «Автоматический»
Нажмите кнопку «Применить» и «ОК».
В ситуации, когда служба работает, а доступа к сети нет, должны помочь следующие действия:
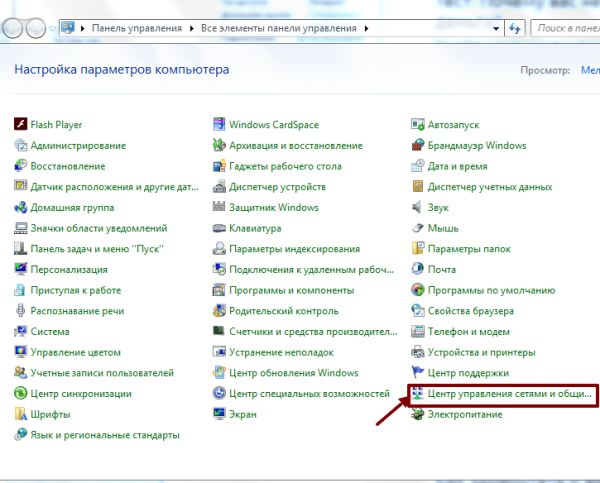
- Войдите в панель управления, там откройте вкладку: «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом».
Откройте вкладку «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом» в окне панели управления Windows
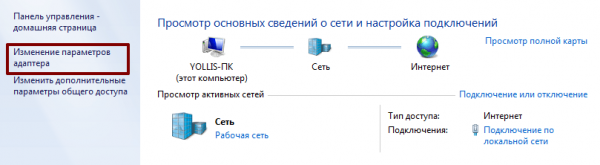
Выберите пункт «Изменение параметров адаптера» в разделе «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом»
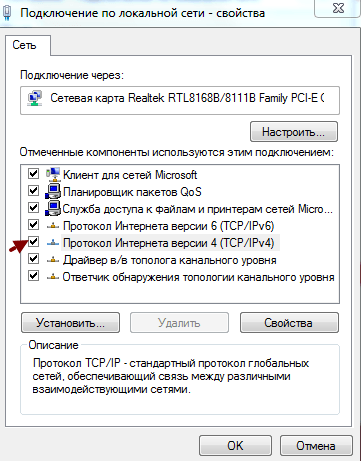
На вкладке «Подключение по локальной сети», выберите пункт «Свойства»
Выделите пункт «Протокол интернета 4 (TCP/IP 4)», нажмите «Свойства»
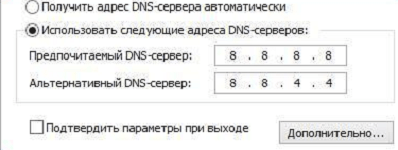
Установите IP адрес сервера в ручном режиме
Если все сделано правильно, а положительного результата нет, существует большая вероятность ошибок Windows. Попробуйте провести восстановление системы в последней точке, когда все работало корректно. Для этого войдите в меню «Пуск», «Панель управления», «Восстановление». Выберите точку восстановления, запустите процедуру, перезагрузите компьютер.
Если браузер продолжает выдавать ошибку, как вариант для решения проблемы возможны такие действия:
- Войдите в «Сетевые подключения», посмотрите нет ли там подозрительных подключений, если вы нашли такое, его необходимо удалить.
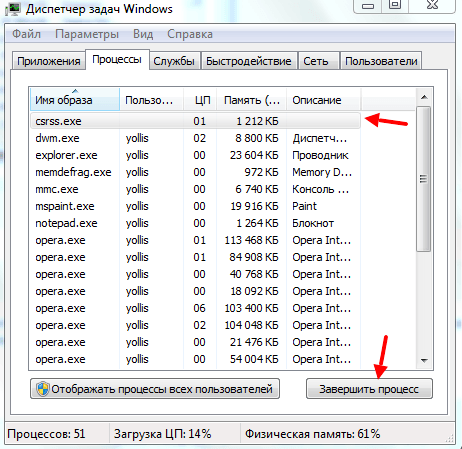
Найдите и удалите подозрительные сетевые подключения
Последовательое завершение процессов через «Диспетчер задач Windows»
Такие манипуляции помогут выявить приложение, мешающее нормальной загрузке сайтов.
Ещё одной причиной ошибки могут быть устаревшие драйверы сетевого адаптера. Найдите его модель. На сайте производителя загрузите новые программы, установите.
Если ничего, из перечисленного выше, не помогло, тогда ваш компьютер атакован вирусом, произведите следующие действия:
Стоит отметить ещё одну ошибку. Иногда при попытке входа в интернет можно увидеть надпись: «Не удаётся преобразовать DNS адрес сервера». Наиболее часто ошибка связана с ремонтными работами на DNS сервисе, предоставляющем услуги доступа к сети. Проверьте соединение с интернетом, подключив к нему другой компьютер или ноутбук. Если ошибка появляется на всех устройствах — свяжитесь с провайдером. В случае когда ошибка свойственна одному устройству, ваши действия подобны к исправлению ошибки «нет доступа к DNS серверу». Ваша система, по-видимому, посылает некорректные запросы на сервер DNS.
Ошибки программного обеспечения
К подобным относятся сбои DNS вызванные ошибками программного обеспечения серверов и отдельных сайтов.
Произошла временная ошибка DNS
Это сообщение вызвано проблемами DNS в Exchange 2013. Microsoft Exchange Server — программный продукт служащий для обмена сообщениями и совместной работы. Не совсем ясно, что обозначает «Временная ошибка сервера. Повторите попытку позже. PRX 3». В конце — есть ещё PRX 1, PRX 3, PRX 7. Документации, к сожалению, нет.
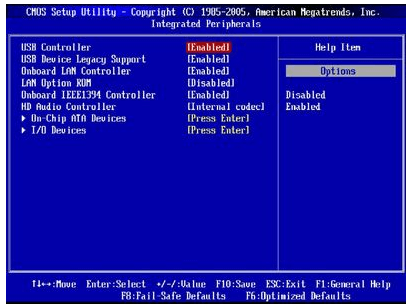
Известны разные способы решения проблемы. Если у вас на компьютере есть встроенная сетевая карта, а дополнительно установленна внешняя, отключите ту, которая не используется. Для этого вам необходимо произвести следующие действия:
Панель БИОС, через которую вносятся изменения в конфигурацию ооборудования
Будьте осторожны, если у вас нет уверенности в своих действиях, не экспериментируйте с БИОС компьютера, лучше пригласите специалиста.
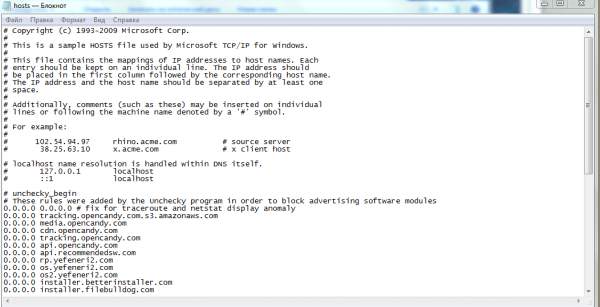
Когда сетевая карта одна или отключение второй не помогло убрать ошибку — попробуйте предпринять такие действия:
Файл hosts предназначен для сопоставления доменных имен сайтов и IP адресов
Не удалось разрешить DNS имя контроллера домена
Специфическая ошибка, редко встречающаяся рядовым пользователям ПК. Характерна для систем, входящих в доменные сети Windows под управлением Active Directory. AD представляет набор процессов и сервисов, позволяет централизованно управлять инфраструктурой локальной сети. Все компьютера сети при этом объединены в общий домен. Ошибка возникает при попытке ввести новый сервер в домен. Система выдаёт сообщение «не удалось разрешить DNS — имя контроллера домена».
Попытайтесь предпринять следующие действия:
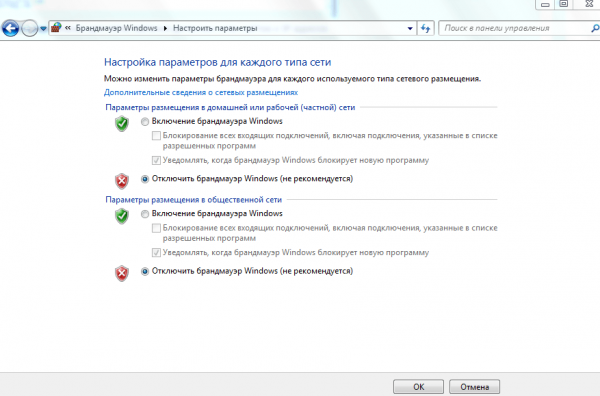
- отключите брандмауэр, возможно, он неправильно настроен;
Отключите Брандмауэр Windows в разделе настройка параметров сети
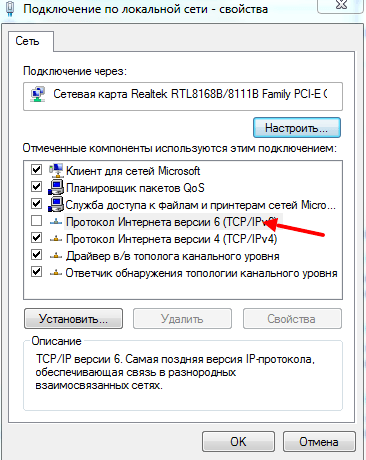
Отключите протокола интерета 6 (TCP/IPv 6) на вкладке свойства сети
Не смогли загрузить страницу потому, что не нашли сайт в dns
Ошибка в основном относится к работе веб-мастеров. При регистрации нового домена DNS серверам неизвестен его адрес. Пока информация о нём на DNS серверах не появится, сайт, почта, другие элементы работать не будут. DNS сервер, прописанный для домена, выступает в роли «глашатая», благодаря которому адрес сайта станет известен другим серверам. Сначала информация о домене появляется на DNS хостинга. Если вы владелец сайта, а при попытке его открыть высвечивается ошибка «на dns сервере не найден адрес для домена этого веб-узла», обратитесь к администрации вашего хостинга.
Подобная ошибка может возникнуть при переносе домена на другой хостинг. В этом случае доменное имя сайта прежнее, а IP адрес меняется. Для решения проблемы необходимо обратиться к администрации вашего хостинга.
Другие распространённые ошибки
Кроме уже рассмотренных, могут возникнуть другие неполадки, связанные, с DNS сервером.
Таблица: часто встречающиеся ошибки DNS и способы их устранения
| Идентификатор события | Сообщение об ошибке | Возможные ошибки и корректирующее действие |
| 408 | Сервер DNS не может открыть сокет для адреса IP. Убедитесь, что это один из действительных адресов компьютера сервера. | Если адрес IP является действительным, проверьте, не пытается ли другое устройство или программа использовать порт службы DNS (53). |
| 413 | Сервер DNS будет отправлять запросы другим серверам DNS на порт, отличный от принятого по умолчанию (TCP порт 53). | Эта проблема возникает на компьютерах с несколькими сетевыми адаптерами (когда сервер DNS настроен на использование только части из доступных адресов IP). Кроме этого, может оказаться, ответы удалённых серверов DNS пытаются использовать порт, использование которого не настроено на локальном сервере DNS, что приводит к возникновению проблем в репликации данных зоны через соединения WAN (сквозь брандмауэры). Для обеспечения использования настроенного порта для всех соединений, измените настройку интерфейсов IP таким образом, чтобы выполнялось одно из условий: Используются все адреса IP. Используется только один из адресов IP. |
| 414 | Компьютер сервера не имеет настроенного основного суффикса DNS. | Например, сервер имеет имя dns 1 вместо dns1.company.net. Эта конфигурация может привести к некорректным или неудачным обращениям. Для исправления этой проблемы подключите сервер DNS к домену или предоставьте полное имя DNS, которое окажется подходящим для рабочей группы. |
| 708 | Сервер DNS не обнаружил первичных или вторичных зон. Сервер запускается в режиме только кэширования и он не авторитетен ни для одной из зон. | Если создание только кэширующего сервера DNS было главной целью, то делать ничего не нужно. В противном случае это сообщение подразумевает необходимость настройки зон на сервере. |
| 3150 | Сервер DNS записал новую версию зоны «zonename» в файл filename. Новую версию можно просмотреть, перейдя на вкладку. | Это событие возникает, когда сервер DNS настроен на работу в качестве корневого сервера. Если это нежелательный результат, необходимо удалить корневую зону (.) для исключения появления таких сообщений. |
| 6527 | Срок действия зоны «zonename» истёк до успешной передачи зоны или обновления с основного сервера, который является источником зоны. Зона была отключена. | Вторичный сервер DNS потерял сетевое соединение с основным сервером, поэтому невозможно выполнить репликацию. Решите проблему в работе сети. На вторичном сервере удалите и повторно создайте зону, указав правильный адрес IP для того же или нового основного сервера. На основном сервере указана неправильная конфигурация зоны в записи SOA. Исправьте это с помощью одного из предложенных действий. Убедитесь, что значение Refresh Intervals меньше, чем значение Expires After. Уменьшите значение Retry Interval. Увеличьте значение Expires After. Добавьте вторичный сервер в список уведомления (Notify List). |
С первого взгляда проблемы, перечисленные в статье, кажутся сложными и почти нерешаемыми. Но тщательно разобравшись в теме, все можно исправить собственными силами. Для этого потребуется терпение и время. Но главное, что вам необходимо, — это желание.
I use Remote Desktop Connection Manager to RDP to my lab PCs. One particular PC wouldn’t connect via this method even though the PCs was up and running on the network.
Using Remote Desktop Connection (mstsc.exe) to connect via the PCs IP address, I could connect. Further troubleshooting showed me that I couldn’t ping or map a drive to this PC either.
The error I was getting in Remote Desktop Connection Manager was “DNS Name Lookup Failure”. Checking DNS on my domain controller showed that the PC was indeed in DNS.
Ploughing through my network adaptor settings, I came across Control PanelNetwork and InternetNetwork ConnectionsEthernet ConnectionPropertiesInternet Protocol Version 4 PropertiesAdvancedWINS
The default is “Use NetBIOS setting from DHCP server. If static IP address is used or the DHCP server does not provide NetBIOS setting, enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.”
After enabling NetBIOS over TCP/IP I was able to connect via RDP, map and otherwise communicate with this server properly again.
You can also change this setting via PowerShell, unfortunately I wasn’t able to find anything in V3 that did this, so you have to use WMI, this blog post goes through the steps on how to do it.
I am in the midst of performance testing a web application and I get these errors in Apache logs
[Sat Apr 18 03:01:01 2015] [error] [client xx.xx.xxx.253] proxy: DNS lookup failure for: jboss-host-name returned by /some/url, referer: http://f5hostname/context/URI
It occurs only at high load levels which indicates that it may not be the configuration that is causing it. I have seen posts where this error occurs due to incorrect proxy configuration, but my case doesn’t fall under that I guess. At the very end of the test I get another error — «All workers are in error state». I think the first DNS error causes all workers to shutdown.
Can someone point where I could start looking? Please let me know if you need more details than whats mentioned below.
More details:
I have an F5 in front of two Apache servers. There are ten JBoss servers in the balancer.
Apache configuration snippet: (I am not using proxypass, just modcluster)
Easiest Way To Fix DNS Lookup Failed Error
“ DNS Lookup Failed” is quite common when you are using Google Chrome. This issue commonly arises when the settings are incorrectly configured or the DNS server stops responding. It’s always recommended to choose the Best DNS Servers for Your Computer.
What does DNS Server Do?
It translates domain names (eg: google.com ) to IP Addresses.
How To Fix DNS Lookup Failed error?
By Default in most computers, DNS server addresses are obtained automatically. You need to change it and use open DNS. It’s recommended to use Google DNS. i.e 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 Or you can find the best DNS servers for your computer.
Once you change the DNS server addresses, restart your computer. Clear cookies, Cache, Browsing History from your browser settings. Try to disable add-ons and see if its works. If you still get a problem try to use in private browsing.
If all the above steps fail, go to Google Chrome settings, Click on show advanced settings and under privacy you would find “Use a web service to help resolve navigation errors” just remove the tick from the checkbox next to it and restart chrome.
If the problem is resolved great or else follow the second method.
Check out this simple video which explains the procedure to change DNS address
2nd Method:
Learn How To Change Dns Server Address on Your Computer: https://developers.google.com/speed/public-dns/docs/using If you have any doubts on how to change it,do let me know by commenting. Share your views on it as we are eagerly waiting. Get More Information About DNS:
PCPedia Recommends DNS For Dummies
OpenVPN Support Forum
Community Support Forum
Post by winter.tal » Tue Nov 01, 2016 7:08 pm
I have been trying to log in to my VPN from mac, and been getting the following error:
Unexpected error: DNS lookup failed on host ‘ ‘ [Errno 8] nodename nor servname provided, or not known
Post by TinCanTech » Tue Nov 01, 2016 8:29 pm
Post by john.skinner@iostudio.com » Fri Nov 18, 2016 4:10 pm
I would assume TinCanTech’s answer didn’t help, as we are having issues with this among our users.
OpenVPN support has informed me that they have seen issues reported from others, with their current Mac OpenVPN Connect client for Mac OS X and Comcast DNS. You can get around this issue if you do not use Comcast DNS on your router or computer. OpenVPN support has had my ticket about this unresolved since October 3rd.
The strange issue is, the computer that the OpenVPN Connect client is installed on has no problem resolving DNS to connect to the OpenVPN Access Server’s client web interface. But when you start the OpenVPN Connect client and attempt to connect to the OpenVPN Access Server, the client has DNS errors resolving the DNS to the OpenVPN Access Server. There is no logs on the Access Server for this because the client can not even resolve the Access Servers address. It seems like something is wrong with the OpenVPN Connect client if it can not resolve the DNS correctly.
Frustrated and puzzled.
Post by TinCanTech » Fri Nov 18, 2016 6:58 pm
If you think this is a bug with Openvpn-Connect then should report it on the bug trac, where you can also follow any progress.
Post by zedd45 » Wed Jan 04, 2017 4:21 pm
I encountered this issue after upgrading to Mac OSX Sierra.
My coworkers did not encounter this issue. Two things to note here that may have contributed to this problem, but which I was unable to confirm where the root cause of the issue:
1. my DNS was provided through AT&T / default ISP settings
2. The DNS for AT&T used an IP6 address
Post by jwilmot » Thu Jan 12, 2017 10:05 pm
Post by fuzzymazoid » Tue Feb 28, 2017 4:11 pm
I just had a user run into the same problem. He just got a new Mac at home, and today was his first day connecting to the office VPN. Symptoms are exactly the same as above: latest Mac OS, Comcast DNS, «Unexpected error: DNS lookup failed on host xxxxxxx: [Errno 8] nodename nor servname provided, or not known»
We had him switch from Comcast DNS servers to Google DNS servers and he was able to connect without issue.
Seems unlikely that Comcast’s DNS is wrong somehow. Is there a bug reported for OpenVPN Connect that we can track?
Post by tmacpherson » Thu Mar 09, 2017 9:52 pm
Post by SomeGuy » Thu Mar 09, 2017 10:50 pm
Two suggestions related to this.
* IPv4 vs IPv6, DNS and resolver affinity: If running a with an openvpn client configuration that has a «server» line with a FQDN (fully-qualified-domain-name) that can resolve to IPv6 and IPv4 addresses, check to see if the OpenVPN server you are trying to connect to provides service for IPv4 and IPv6 clients. Many resolvers in OS have an affinity to resolve DNS AAAA records over A or CNAME, and will tend to favor IPv6 addresses being resolved for a name to IP if there are both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses available.
* Domains that support DNSSec : many ISP are moving to apply rules of DNSSec with name-to-IP lookups n the DNS Servers *they* run for their customers. If another domain name is poorly configured with DNSSec, or has expired keys, properly enforcing DNS Servers completing your query against DNS that have DNSSec configured will NOT pass on any IP addresses to their customers because the results can’t be validated. Some ISP have experimented with partial DNSSec support, or a kludgy redirection to a web page that tells the *web* client that the attempt to resolve the name to an IP resulted in DNSSec problems. Such a web page would not be visible to «you» if your OpenVPN client is being redirected to a different IP than what is expected.
I know Comcast was early to experiment with DNSSec and adopt use of IPv6. Would anyone that encounters the problem described in this thread please check to see if any of these above items are the source of troubles? Some suggested methods to test are listed below:
DNS lookups, IPv4 vs IPv6 or some other DNS issue: If you have a linux shell with «dig» installed.
In these examples, I am using «8.8.8.8» (google’s public DNS Server’s IPv4 IP address) and 2001:4860:4860::8888 (google’s public DNS Server’s IPv6 IP address.)
The «-4» says, use my IPv4 IP address and connect to the IPv4 address of the server (useful if you use names instead of IP addresses for which DNS Server you want to use) and the «-6» says use an IPv6 IP address on my machine to talk to a DNS running with an IPv6 address. (Using an IPv4 address for DNS after the «@» already requests IPv4 implicitly, but including in case you replace the value after the «@» with a name.)
The «A» is conventionally a record for name to IPv4 address.
The «AAAA» is a record for name to IPv6 address.
Query Google’s IPv6 DNS Server, and ask for an AAAA record (IPv6 address, if any) for the host name «www.google.com»:
In this case, a CNAME resolves to a name, which you could then resolve, and follow until you find the IP address.
If any of the intermediate CNAME in the chain to your final IP address use DNSSec, then those domains may also need to be investigated for proper configuration.
Next, try the same against your ISP’s provided DNS servers and replace the valued after the «@» with your ISP’s DNS Server IP. Do you get the same results?
If the results do not match what you see from google’s DNS, how are they different? Does one resolve to an IP while the other does not? Do they resolve to different IP? If different, who owns the netblock of the IP address that is an unexpected result?
Next, tools for DNSSec checks. less likely as a cause, but possible:
If your domain uses delegation with sub-domains, then you may need to check your domain name, *and* sub-domains for proper DNSSec configurations, all the way up to, but not including a hostname for each sub-domain delegation with DNSSec.
If you find that CNAME were uses to other names in the top step, you will want to check the DNSSec status of those domains and/or sub-domains until you finally reach an IP address.
If you find that the problems you are encountering are not related to these two issues (IPv6 address resolved vs IPv4 address resolved, OR DNSSec validation/configuration issues) please follow-up saying so.
If you find that one or both are the source of trouble, please also post that information.
Knowing what the source of the problem is would help to know if this is a bug or not, and if not, how to fix it or side-step it.
I have not had any problems with client resolution on Comcast or Verizon, or Sprint, or AT&T when I used them, but I use properly configured domains using DNSSec for my domains to validate hosts, support dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 with service for both for each server name and port.
Post by teec » Tue May 09, 2017 1:01 pm
Have you had any updates on this issue? It prevents me from accessing my work VPN from home. Yes, the Google DNS change helps, but then screws up my DNS while at work so I don’t want to have to keep switching back and forth. This issue only arose for me after upgrading to OSX Sierra..
Post by maxigs » Wed May 17, 2017 8:54 am
Another one here. I upgraded to sierra yesterday and have the same issue now trying to log on the company VPN.
I «fixed» it for now by adding the hostname to my /etc/hosts file to skip resolving it. This seems to work for now, not ideal but the IP rarely changes so i can live with it.
Post by vcardillo » Mon May 22, 2017 9:03 pm
Post by Gushi » Wed Jul 19, 2017 12:41 am
No, and we’re using the appliance with a paid license (which means, in theory, that our issues should get some kind of support).
I’ve captured packets of my mac doing a DNS lookup and explicitly requesting a AAAA record to my local DNS server. The connection then fails, instead of falling back to asking for an A record.
Post by lawrence.henry » Fri Sep 01, 2017 1:15 pm
See notes below to disable and re-enable ipv6:
You can also combine both of those commands into a single string to disable both wireless and ethernet, just use the following syntax:
Be sure to enter that string onto a single line to issue the command properly.
Re-Enabling IPv6 for Wi-Fi & Ethernet in OS X
Of course, reversing the above change is also possible, and you can re-enable IPV6 support with the following command strings entered into the terminal:
You can also place this into a single command to re-enable IPv6 for Wi-Fi and ethernet like so:
SomeGuy wrote: Two suggestions related to this.
* IPv4 vs IPv6, DNS and resolver affinity: If running a with an openvpn client configuration that has a «server» line with a FQDN (fully-qualified-domain-name) that can resolve to IPv6 and IPv4 addresses, check to see if the OpenVPN server you are trying to connect to provides service for IPv4 and IPv6 clients. Many resolvers in OS have an affinity to resolve DNS AAAA records over A or CNAME, and will tend to favor IPv6 addresses being resolved for a name to IP if there are both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses available.
* Domains that support DNSSec : many ISP are moving to apply rules of DNSSec with name-to-IP lookups n the DNS Servers *they* run for their customers. If another domain name is poorly configured with DNSSec, or has expired keys, properly enforcing DNS Servers completing your query against DNS that have DNSSec configured will NOT pass on any IP addresses to their customers because the results can’t be validated. Some ISP have experimented with partial DNSSec support, or a kludgy redirection to a web page that tells the *web* client that the attempt to resolve the name to an IP resulted in DNSSec problems. Such a web page would not be visible to «you» if your OpenVPN client is being redirected to a different IP than what is expected.
I know Comcast was early to experiment with DNSSec and adopt use of IPv6. Would anyone that encounters the problem described in this thread please check to see if any of these above items are the source of troubles? Some suggested methods to test are listed below:
DNS lookups, IPv4 vs IPv6 or some other DNS issue: If you have a linux shell with «dig» installed.
In these examples, I am using «8.8.8.8» (google’s public DNS Server’s IPv4 IP address) and 2001:4860:4860::8888 (google’s public DNS Server’s IPv6 IP address.)
The «-4» says, use my IPv4 IP address and connect to the IPv4 address of the server (useful if you use names instead of IP addresses for which DNS Server you want to use) and the «-6» says use an IPv6 IP address on my machine to talk to a DNS running with an IPv6 address. (Using an IPv4 address for DNS after the «@» already requests IPv4 implicitly, but including in case you replace the value after the «@» with a name.)
The «A» is conventionally a record for name to IPv4 address.
The «AAAA» is a record for name to IPv6 address.
Query Google’s IPv6 DNS Server, and ask for an AAAA record (IPv6 address, if any) for the host name «www.google.com»:
In this case, a CNAME resolves to a name, which you could then resolve, and follow until you find the IP address.
If any of the intermediate CNAME in the chain to your final IP address use DNSSec, then those domains may also need to be investigated for proper configuration.
Next, try the same against your ISP’s provided DNS servers and replace the valued after the «@» with your ISP’s DNS Server IP. Do you get the same results?
If the results do not match what you see from google’s DNS, how are they different? Does one resolve to an IP while the other does not? Do they resolve to different IP? If different, who owns the netblock of the IP address that is an unexpected result?
Next, tools for DNSSec checks. less likely as a cause, but possible:
If your domain uses delegation with sub-domains, then you may need to check your domain name, *and* sub-domains for proper DNSSec configurations, all the way up to, but not including a hostname for each sub-domain delegation with DNSSec.
If you find that CNAME were uses to other names in the top step, you will want to check the DNSSec status of those domains and/or sub-domains until you finally reach an IP address.
If you find that the problems you are encountering are not related to these two issues (IPv6 address resolved vs IPv4 address resolved, OR DNSSec validation/configuration issues) please follow-up saying so.
If you find that one or both are the source of trouble, please also post that information.
Knowing what the source of the problem is would help to know if this is a bug or not, and if not, how to fix it or side-step it.
I have not had any problems with client resolution on Comcast or Verizon, or Sprint, or AT&T when I used them, but I use properly configured domains using DNSSec for my domains to validate hosts, support dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 with service for both for each server name and port.