Economic moat что это
Economic Moat
What is an Economic Moat?
Conceptualized and named by Warren Buffett, an economic moat is a distinct advantage a company has over its competitors which allows it to protect its market share and profitability. It is often an advantage that is difficult to mimic or duplicate (brand identity, patents) and thus creates an effective barrier against competition from other firms.
Moat: My Favorite Financial Term
Understanding an Economic Moat
Every successful company understands that the main threat to their continued success will be from competitors, and keeping them at bay is critical to sustaining their dominance. With the passage of time, they are likely to see an erosion to their bottom line as competitors eat away at their market share. Which is why a business that intends to remain dominant has to establish an economic moat. Economic moat describes a company’s competitive advantage derived as a result of various business tactics that allow it to earn above-average profits for a sustainable period of time.
This is important not only to the company’s bottom line but also to potential investors seeking to maximize their portfolios by including companies that will maintain their performance edge. By establishing a defensible competitive advantage a company can fashion a wide enough economic moat that effectively curbs competition within their industry. Essentially, the wider the economic moat, the larger and more sustainable the competitive advantage of a firm.
An intangible asset, such as a company crafting a well-known brand name (Nike), pricing power edge (Apple), cost advantages (Walmart), making it costly for customers to switch products (cell phone companies), efficient scale, and network effects are all advantages that businesses can utilize to create a wide economic moat.
The most obvious financial characteristics that companies with a wide economic moat have is that they usually generate large amounts of free cash flow and have a track record of strong returns.
Key Takeaways
Sources of Economic Moats
A company that is able to maintain low operating expenses in relation to its sales compared to its peers has cost advantages, and it can undercut its competition by lowering prices and keeping rivals at bay. Consider Wal-Mart Stores Inc., which has an immense volume of sales and negotiates low prices with its suppliers, resulting in low-cost products in its stores that are hard to replicate by its competitors.
Intangible assets refer to the patents, brands and licenses that allow a company to protect its production process and charge premium prices. While brands are typically derived from superior product offerings and marketing, patents are obtained as a result of companies’ filings with governments to protect know-hows for a specific period of time, typically 20 years. Pharmaceutical companies earn high profits due to patented drugs after spending billions on research and development.
Efficient scale arises when a particular market is best served by a limited number of companies, giving them near monopoly statuses. Utility firms are examples of companies with efficient scale that is necessary to serve electricity and water to their customers in a single geographic area. Building a second utility company in the same area would be too costly and inefficient.
Switching costs is another type of economic moat, which make it very time-consuming and expensive for consumers to switch products or brands. Autodesk Inc. offers various software solutions for engineers and designers that are very difficult to learn. Once an Autodesk customer starts using its software, he is unlikely to switch, allowing Autodesk to charge premium prices for its products.
The network effect can further fortify a company’s economic moat by making its products more valuable the more people use them. An example of a network effect is online marketplaces such as Amazon and eBay, which are widely popular among consumers because of the large quantity of people buying and selling various products through their platforms.
Экономический ров (Wide Moat) — инвестиции в компании с конкурентным преимуществом
Что такое экономический ров
Wide Moat можно сравнить со средневековым замком, окруженным рвом наполненным водой. Чем шире ров, тем труднее противнику (конкурентам) захватить замок (отвоевать долю рынка).
Источники Wide Moat
«Я хотел бы владеть компанией Порше. Её клиенты против того, чтобы эта машина стоила дёшево.»
Патент на уникальное лекарство, позволяя компании оградить свой бизнес от конкурентов. Давая возможность генерировать прибыль долгие годы.
Преимущество в затратах. Низкая себестоимость производства. Например, удачное расположение, дешевый способ добычи или близость к уникальным ресурсам (Норникель, НМТП, Полюс Золото). Субсидии от государства (Газпром, Роснефть).
Издержки перехода. Когда переход от одного поставщика продукции к другому, требует значительных издержек (финансовых и временных). Пример, Oracle.
Сетевые рвы. Чем больше людей пользуются продуктом (услугой, сервисом), тем шире и сильнее ров (Amazon, eBay, Facebook, Mastercard).
Преимущества компаний с Wide Moat
Наличие экономического рва позволяет компании развиваться в более комфортных условиях.
Высокая рентабельность бизнеса. Стабильный денежный поток.
Низкая долговая нагрузка.
Способность более легко переносить тяжелые времена в экономике. За счет постоянного денежного потока. Как следствие такие компании имеет более низкую вероятность банкротства.
Возможность поднимать цены на свою продукцию. Без сильных рисков потери клиентской базы.
И самое главное, имея преимущество перед конкурентами, компании с экономическим рвом, способны обеспечить инвесторов прибылью на долгие годы. За счет роста акционерного капитала (котировок) и выплачиваемых дивидендов.
Как найти компании с широким рвом?
Нужно посмотреть на показатели бизнеса компании (мультипликаторы) за несколько последних лет. Чтобы понять, действительно ли компания имеет преимущество перед остальными конкурентами.
А вот если рассматривать американский или мировой рынок? Несколько тысяч компаний. Большинство названий ни о чем не скажет инвестору.
Можно ориентироваться на бренд (известность) компании. И строить выбор исходя из этого.
Есть такой сервис Интербренд. Сайт по своим формулам рассчитывает силу бренда компании. И выводит его некую субъективную стоимость.
Готовое решение
На рынке все уже придумано за нас. И почему бы этим не воспользоваться.
Речь идет про ETF. Со стратегией выбора компаний с Wide Moat (широким рвом).
Стратегия ETF MOAT. Среди компаний с широким экономическим рвом, выбираются имеющие справедливую стоимость на рынке.
ETF был запущен в 2013 году. И за это время (хотя это не показатель на таких малых сроках) показал доходность выше, чем индекс S&P 500.
Если вы не можете (или не хотите) покупать ETF. Например, торгуете только на бирже Санкт-Петербурга (СПБ). Что делать?
Смотрим состав фонда (по ссылке). На момент написания статьи имеем 52 компании. Которые по мнению провайдера имеют широкий экономический ров и (самое главное) адекватную стоимость на рынке.
Что в составе из известного?
В итоге список еще может уменьшится раза в два.
Резюмируя
Чем сильнее Wide Moat, тем эффективнее барьер от конкурентов.
Компании с широким экономическим рвом имеют возможность генерировать большие объемы свободного денежного потока и прибыли долгие годы.
Economic Moat
What is an Economic Moat?
The term “economic moat” refers to a long-term competitive advantage Competitive Advantage A competitive advantage is an attribute that enables a company to outperform its competitors. It allows a company to achieve superior margins that a company holds that protects its position in the marketplace. The term is inspired by the moat that surrounded medieval castles to protect the valuables within from invaders. A company with a strong moat possesses a competitive advantage that is both strong and sustainable.
Investors such as Warren Buffet state that buying businesses is like buying castles. Buffett emphasizes the importance of buying businesses with deep moats, as they are protected from competitors and can, therefore, maintain strong profits.
Why is an Economic Moat Important to Investors?
Two things that investors generally care about are the magnitude of return in excess of the cost of capital Cost of Capital Cost of capital is the minimum rate of return that a business must earn before generating value. Before a business can turn a profit, it must at least generate sufficient income to cover the cost of funding its operation. and how long the company can be expected to continue to generate large returns. To begin generating large profits, a company must first achieve a competitive advantage. The advantage can come from any of a number of things – lower production costs, patents, high switching costs – any one of which can be especially helpful in differentiating a company from its competitors and in retaining its customer base.
To sustain profits and be considered a moat, the competitive advantage must be durable. Thus, it can provide value for investors.
Summary
How to Create an Economic Moat?
Economic moats can be created in one of three ways, as follows:
1. Production advantages
A company achieves production advantages when it is able to provide a service at a lower cost than that of its competitors.
Features of companies with production advantages include:
2. Consumer advantages
A company achieves consumer advantages when it is able to provide a greater benefit to consumers than its competitors do.
Features of companies with consumer advantages include:
3. Brand value
Brand value is the idea that a company is able to generate more revenue or charge a premium price because of brand recognition. This is based on the fact that customers believe there is a correlation between well-known brands and quality products. Brand value is especially important for companies that have commodified products.
For example, coffee is a commodified product, so, for coffee shops to attract customers, they need to differentiate themselves through their brand. Starbucks is a company that has capitalized on the brand value its name holds.
The company’s brand is based on convenience, good customer service, and innovative drinks. By developing the brand value over the last decade, Starbucks is now the “go-to” place for coffee and is able to charge a premium for their drinks, which is a strong moat.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI’s Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst.
To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional CFI resources below
Financial Analyst Training
Gain the confidence you need to move up the ladder in a high powered corporate finance career path.
Learn financial modeling and valuation in Excel the easy way, with step-by-step training.
Экономический ров: что создает конкурентное преимущество?
Экономический ров (economic moat) — одна из лучших составляющих успешного бизнеса, которые может иметь компания. Но что он из себя представляет и как помогает поддерживать конкурентное преимущество?
Инвестирование было бы довольно легким делом, если бы все, что вам нужно было сделать, это найти высокодоходные компании и вложить в них деньги. К сожалению, это не так просто. Проблема с компаниями, получающими высокую прибыль, заключается в том, что они быстро создают конкуренцию. Со временем эта конкуренция может уничтожить долю рынка и значительно снизить рентабельность.
Возьмем, к примеру, индустрию моды. Как правило, модный дом создает новый популярный продукт, например, Ugg Boots. Модные магазины определят популярность этого продукта и начинают выпускать свои собственные версии. Эти подделки не только повлияют на продажи оригинала, но и уменьшат эксклюзивность оригинального продукта, поскольку все больше и больше людей начинают их носить.
Однако есть некоторые предприятия, которым удается игнорировать эту тенденцию и которые могут поддерживать высокую прибыль в течение десятилетий, несмотря на конкуренцию. Это потому, что у этих предприятий есть экономический ров — конкурентное преимущество, которое сохраняется в течение длительного периода времени.
Экономический ров в бизнесе компаний
Концепция экономического рва имеет решающее значение для долгосрочных инвесторов. Без него практически невозможно прогнозировать прибыль в ожидаемые сроки.
Вы могли бы с достаточной уверенностью предположить, сколько заработает компания в следующем году, но оценить возможную доходность на следующие десять лет — гораздо более сложная задача. Рвы придают этой прибыли некоторую защиту и помогают нам лучше ориентироваться в будущем компании.
Инвестирование требует долгосрочного взгляда на мир и на те предприятия, которыми вы планируете владеть. Большинство предприятий, с которыми мы когда-либо столкнемся, будут в лучшем случае мгновенным успехом, и часто именно эти раскрученные акции вызывают проблемы у начинающих инвесторов.
Чтобы быть успешными инвесторами, мы должны уметь определять компании, которые смогут поддерживать и процветать в будущем.
Разберем основные типы экономического рва.
Брендовые рвы
Рвы бывают разных форм, и некоторые из них более мощные, чем другие. Самый очевидный из них — тот, с которым мы, как потребители, больше всего знакомы, — это сильный бренд.
Пэт Дорси, автор книги «Маленькая книга, которая создает богатство», утверждает, что эффективные бренды изменяют поведение потребителей, потому что они повышают нашу готовность платить за что-то или снижают наши затраты на поиск.
Tiffany’s (NYSE: TIF) — прекрасный пример бренда, повышающего готовность потребителя платить. На протяжении десятилетий Tiffany’s взимала гораздо больше, чем конкуренты, за один и тот же продукт, и все потому, что эта знаменитая синяя коробка имеет невероятную нематериальную ценность.
Точно так же люди считают, что ношение Nike (NYSE: NKE) или Under Armour (NYSE: UA) улучшит их результаты в спорте и, таким образом, заплатят больше за их продукцию. Устройства Apple (NASDAQ: AAPL), как правило, намного дороже устройств конкурентов (и, возможно, менее продвинуты), но это не мешает людям выкладывать за них гораздо большие деньги.
Бренды также снижают стоимость поиска. Зачем людям доплачивать за Starbucks (NASDAQ: SBUX), если они могут получить более дешевый и лучший кофе в другом месте? Потому что вы знаете, что получаете со Starbucks, и поэтому исключаете риск разочарования. Вы часто найдете людей, которые никогда не зайдут в Starbucks или McDonalds (NYSE: MCD) в своем районе, но у них не возникнет проблем с этим во время путешествий.
Нормативный ров
Патенты имеют большое значение в биотехнологической отрасли и могут создать юридическую монополию для компании на 20 лет. Это означает, что у компании, выпускающей популярный препарат, впереди два десятилетия беспрепятственного взлета, прежде чем истечет срок действия патента и лекарство станет непатентованным.
Точно так же у некоторых компаний есть лицензии, которые защищают их от конкуренции. Операторы казино, такие как Wynn Resorts (NASDAQ: WYNN), получают огромную выгоду от строгих законов о лицензировании на таких территориях, как Макао, которые не позволяют новым конкурентам легко приходить на рынок.
Преимущества по стоимости
Ценовые преимущества — это форма экономического рва, который мы наблюдаем все больше и больше в наши дни с ростом электронной коммерции.
Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN) всегда сможет подорвать позиции традиционных розничных продавцов, поскольку им не нужно платить за аренду магазинов или зарплату продавцам. Изначально Amazon была основана на основании постановления Верховного суда, согласно которому компании должны платить налог с продаж только в тех штатах, где они имеют физическое присутствие. Это означало, что Безос мог продавать книги через Интернет по гораздо более низкой цене, чем у обычных розничных продавцов, таких как Barnes and Noble.
Ровные затраты на переключение
Затраты на переход представляют собой один из самых мощных экономических рвов, поскольку они удерживают клиентов на долгие годы и затрудняют переход к конкуренту.
У Intuit (NASDAQ: INTU) — создателей QuickBooks, Quicken и TurboTax — невероятный ров, несмотря на большое количество конкурентов. Это потому, что они затруднили экспорт данных из своего программного обеспечения в чужое. Мало того, требуется время, чтобы научиться эффективно использовать их программное обеспечение, и поэтому любой бизнес, который хочет перейти на него, должен будет понести дополнительные расходы на обучение.
Сетевой эффект
Наконец, «сетевой эффект» — это своего рода ров, который делает бизнес более ценным, чем больше людей его используют.
Чем больше потребителей имеют карты Mastercard (NYSE: MA), тем больше розничных продавцов их примут. Чем больше розничных продавцов их примут, тем больше людей их получат. Создание такой циклической сети — невероятное преимущество для бизнеса, который сокращает каждую совершаемую нами транзакцию.
Точно так же отдыхающие будут проверять отзывы на TripAdvisor (NASDAQ: TRIP), а затем добавлять свои собственные, что побуждает больше людей посещать сайт. Чем больше людей посещают сайт, тем больше рекламодателей хотят на нем присутствовать.
Подведем итоги
Экономический ров означает, что компания имеет конкурентное преимущество перед отраслевыми соперниками.
Ценовое преимущество означает, что компания может повышать цены на свою продукцию, не наблюдая падения спроса на нее. Компании с экономическим рвом обычно демонстрируют сильную ценовую политику, потому что клиенты ценят услуги, которые они предоставляют.
Некоторые аналитики оценивают компании в зависимости от их предполагаемого экономического положения. Morningstar, например, дает компаниям, зарегистрированным на бирже, экономический рейтинг, основанный на пяти выявленных им источниках: затраты на ведение бизнеса, сетевой эффект, нематериальные активы и рентабельность.
What Is an Economic Moat?
What Is an Economic Moat?
The term economic moat, popularized by Warren Buffett, refers to a business’ ability to maintain competitive advantages over its competitors in order to protect its long-term profits and market share from competing firms. Just like a medieval castle, the moat serves to protect those inside the fortress and their riches from outsiders.
Understanding an Econonomic Moat
Remember that a competitive advantage is essentially any factor that allows a company to provide a good or service that is similar to those offered by its competitors and, at the same time, outperform those competitors in profits. A good example of a competitive advantage would be a low-cost advantage, such as cheap access to raw materials. Very successful investors such as Buffett have been adept at finding companies with solid economic moats but relatively low share prices.
One of the basic tenets of modern economics, however, is that, given time, competition will erode any competitive advantages enjoyed by a firm. This effect occurs because once a firm establishes competitive advantages, its superior operations generate boosted profits for itself, thus providing a strong incentive for competing firms to duplicate the methods of the leading firm or find even better operating methods.
Moat: My Favorite Financial Term
Illustrative Example
Let’s return to the example of a low-cost advantage. Suppose you have decided to make your fortune by running a lemonade stand. You realize that if you buy your lemons in bulk once a week instead of every morning, you can reduce your expenses by 30%, allowing you to undercut the prices of competing lemonade stands. Your low prices lead to an increase in the number of customers buying lemonade from you (and not from your competitors). As a result, you see an increase in profits. However, it probably wouldn’t take very long for your competitors to notice your method and employ it themselves. Therefore, in a short period of time, your large profits would erode, and the local lemonade industry would return to normal conditions again.
However, suppose you develop and patent a juicing technology that allows you to get 30% more juice out of the average lemon. This would have the same effect of reducing your average cost per glass of lemonade. This time, your competitors will have no way of duplicating your methods, as your competitive advantage is protected by your patent. In this example, your economic moat is the patent that you hold on your proprietary technology. In this case, if your lemonade company was a public firm, your common stock would probably outperform that of your competition in the long run.
As you can see, a company’s economic moat represents a qualitative measurement of its ability to keep competitors at bay for an extended period of time. This translates into prolonged profits in the future. Economic moats are difficult to express quantitatively because they have no obvious dollar value, but are a vital qualitative factor in a company’s long-term success or failure and in the selection of stocks.
Creating an Economic Moat
There are several ways in which a company creates an economic moat that allows it to have a significant advantage over its competitors. Below, we will explore some different ways in which moats are created.
Cost Advantage
As discussed in the lemonade stand example, a cost advantage that competitors cannot replicate can be a very effective economic moat. Companies with significant cost advantages can undercut the prices of any competitor that attempts to move into their industry, either forcing the competitor to leave the industry or at least impeding its growth. Companies with sustainable cost advantages can maintain a very large market share of their industry by squeezing out any new competitors who try to move in.
Size Advantage
Being big can sometimes, in itself, create an economic moat for a company. At a certain size, a firm achieves economies of scale. This is when more units of a good or service can be produced on a larger scale with lower input costs. This reduces overhead costs in areas such as financing, advertising, production, etc. Large companies that compete in a given industry tend to dominate the core market share of that industry, while smaller players are forced to either leave the industry or occupy smaller «niche» roles.
High Switching Costs
Being the big fish in the pond has other advantages. When a company is able to establish itself in an industry, suppliers and customers can be subject to high switching costs should they choose to do business with a new competitor. Competitors have a very difficult time taking market share away from the industry leader because of these cumbersome switching costs.
Intangibles
Another type of economic moat can be created through a firm’s intangible assets, which includes items such as patents, brand recognition, government licenses and others. Strong brand name recognition allows these types of companies to charge a premium for their products over other competitors’ goods, which boosts profits.
Soft Moats
Some of the reasons a company might have an economic moat are more difficult to identify. For example, soft moats may be created by exceptional management or a unique corporate culture. While difficult to describe, a unique leadership and corporate environment may partially contribute to a corporation’s prolonged economic success.
Economic moats are generally difficult to pinpoint at the time they are being created. Their effects are much more easily observed in hindsight once a company has risen to great heights.
From an investor’s view, it is ideal to invest in growing companies just as they begin to reap the benefits of a wide and sustainable economic moat. In this case, the most important factor is the longevity of the moat. The longer a company can harvest profits, the greater the benefits for itself and its shareholders.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pic16-9b4adcd4fb7644e98174412f2c3fdebb.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gordonscottphoto-5bfc26c446e0fb00265b0ed4.jpg)

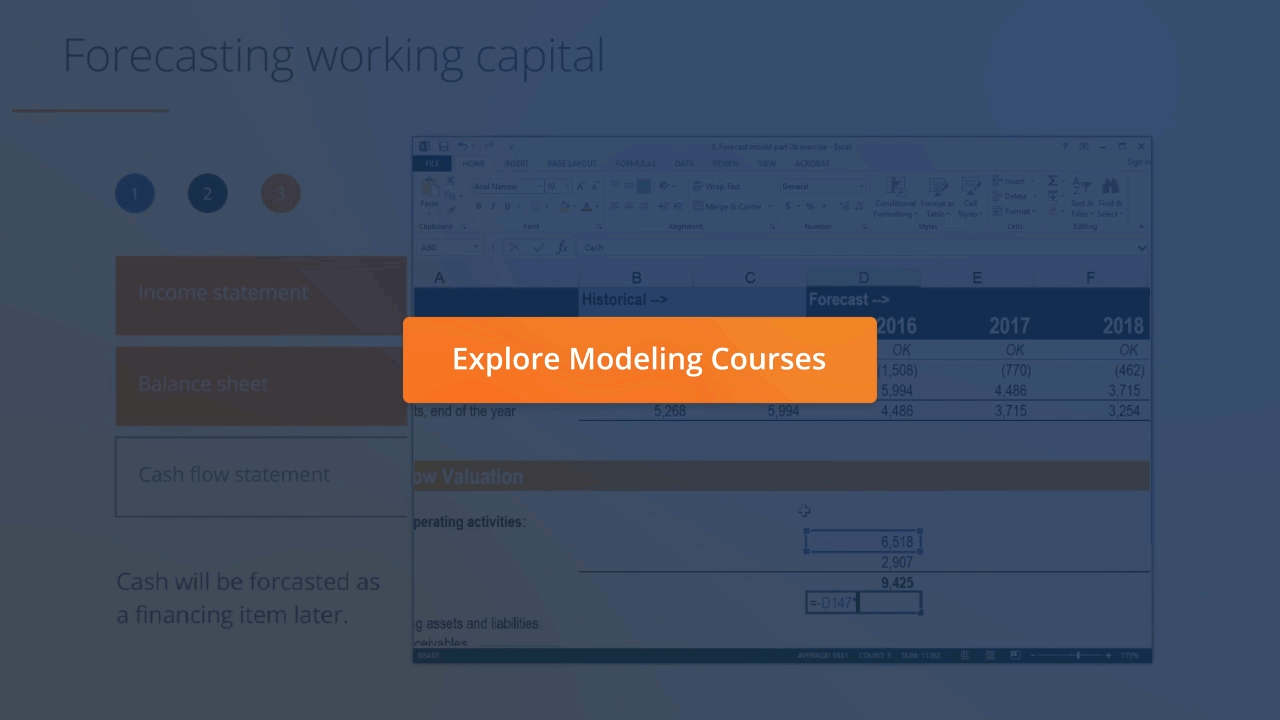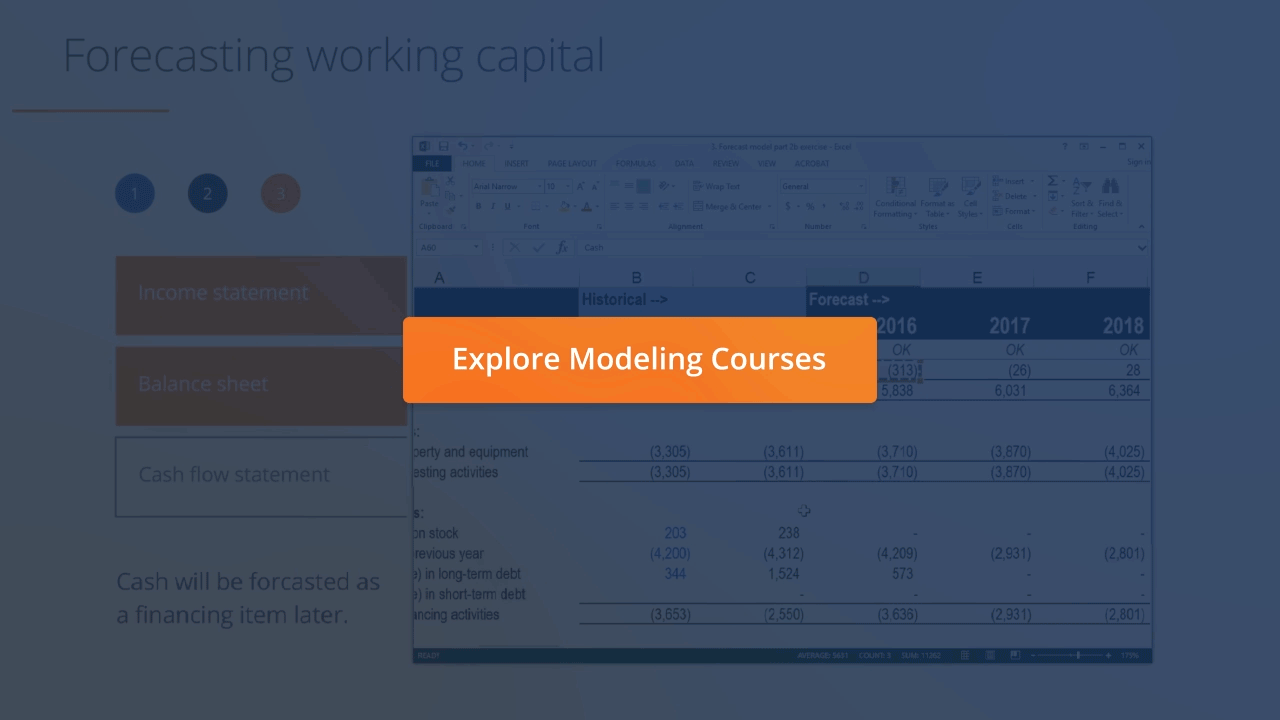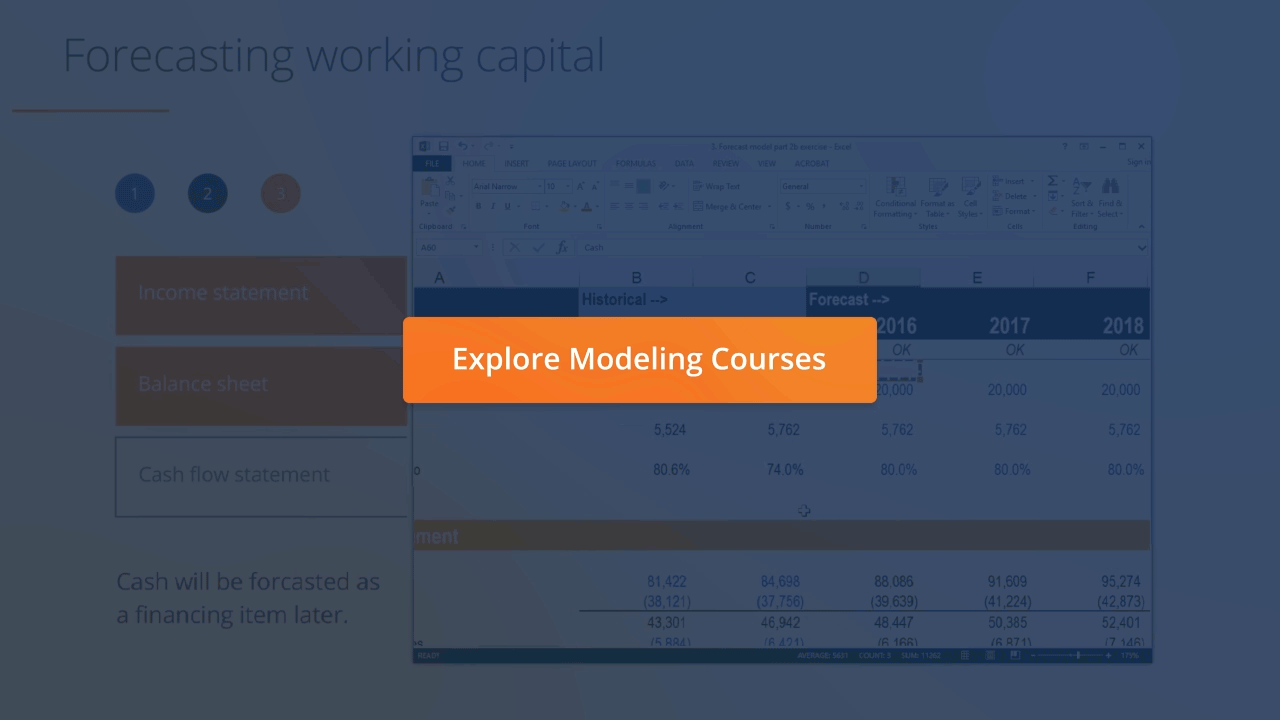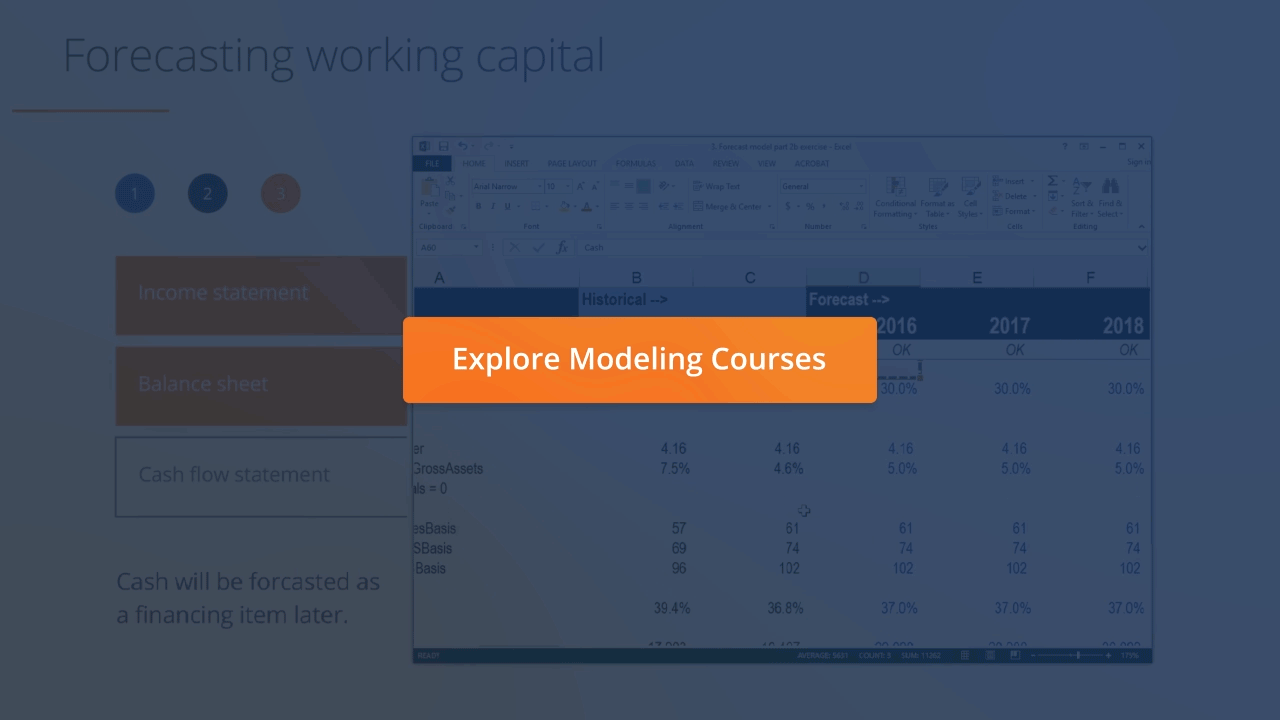

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/image0-MichaelBoyle-d90f2cc61d274246a2be03cdd144f699.jpeg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SuzannesHeadshot-3dcd99dc3f2e405e8bd37271894491ac.jpg)