Eclipse mylyn что это
Mylyn
Mylyn динамически подстраивает интерфейс Eclipse, оставляет только те элементы в дереве ресурсов, которые соответствуют текущей задаче.
Mylyn логически продолжает такие «диалоги», как «Go Into», «Open Associated Perspective?»
См. также
 |
 Eclipse Foundation Eclipse Foundation | |
|---|---|
| AspectJ · BIRT · Buckminster · Eclipse · Equinox · EclipseLink · SWT · Mylyn · Jetty · JFace · Rich AJAX Platform · Virgo | |
| Лицензия: Eclipse Public License · Вебсайт: http://www.eclipse.org/ |
Полезное
Смотреть что такое «Mylyn» в других словарях:
Mylyn — Aktuelle Version 3.6.2 (23. September 2011) Betriebssystem Eclipse in der Java Laufzeitumgebung Kategorie Entwicklungswerkzeug Lizenz EPL … Deutsch Wikipedia
Mylyn — est le nom d un sous système d Eclipse s occupant de la gestion des tâches. Le nom du projet est inspiré du mot anglais myelin (myéline), nom de l isolant gainant les axones pour éviter la dispersion de l influx nerveux. Le projet veut en effet… … Wikipédia en Français
Mylyn — Eclipse Mylyn Project Developer(s) Eclipse Foundation Stable release 3.6.2 / September 23, 2011; 53 days ago (2011 09 23) Written in Java … Wikipedia
Comparison of issue-tracking systems — This article is a comparison of issue tracking systems which are notable, including bug tracking systems, help desk and service desk issue tracking systems, and asset management systems. The comparison includes client server application,… … Wikipedia
Mik Kersten — Born 23 June 1975 Warsaw, Poland Residence Vancouver, Canada … Wikipedia
List of Eclipse projects — The following is a list of notable projects and plugins for the Eclipse IDE.Official Eclipse projectsThese projects are maintained by the Eclipse community and hosted by the Eclipse Foundation.Core projects* Rich Client Platform (… … Wikipedia
Eclipse (среда разработки) — У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Eclipse. Eclipse … Википедия
Eclipse-Plugin — Eclipse Eclipse mit Wiki Plugin Basisdaten … Deutsch Wikipedia
Eclipse (Software) — Eclipse Eclipse mit Wiki Plugin Basisdaten … Deutsch Wikipedia
Eclipse SDK — Eclipse Eclipse mit Wiki Plugin Basisdaten … Deutsch Wikipedia
5 причин полюбить Mylyn
Данный пост на самом деле является инициатором еще одного, который уже выходил ранее. Меня на самом удивило, что о такой интересной вещи, как Mylyn, так мало написано на хабре и мне бы хотелось немного это исправить. Под катом перевод достаточно интересной, на мой взгляд, статьи. Надеюсь на интересное обсуждение.
Современные среды разработки подарили множество средств для ускоренной работы, когда множество действий можно делать всего пальцем. Интеграция редакторов и компиляторов для самых разнообразных языков, средства для работы с базами данных, инструменты разработки специфичные для того или иного фреймворка, а так же многие другие являются уже привычными для нас и основаны на более мелких, но ключевых вещах. Но зачастую в момент интеграции забывают о ключевой части, о конечном пользователе – разработчике.
Созданные на сегодняшний день различные инструменты разработки, с одной стороны надежно работающие, а с другой, не грамотно встроенные в интерфейс, помогают разработчику быть более продуктивным. Тем не менее, с ростом сложности интегрированных средств разработки, только наличие подобных небольших инструментов помогают ориентироваться в возможностях этих систем. В связи с этим современным разработчикам необходима такая среда, которая позволит сосредоточиться только на тех артефактах, которые представляют интерес для пользователя, и, кроме этого, будет отображать только тот функционал системы, который действительно важен пользователю. И здесь на сцене появляется Eclipse и плагин под названием Mylar, позднее переименованный в Mylyn. Mylyn меняет принцип разработки программного обеспечения следующим образом. Вместо того чтобы устанавливать массу инструментов для работы с артефактами, возникающими в процессе разработки, и использовать постфактум, Mylyn помогает обрабатывать эти артефакты в момент создания.
Итак, закрепив эту ключевую мысль в голове, перейдем к более детальному описанию возможностей Mylyn.
Mylyn позволяет вам сконцентрироваться на ваших задачах
Чтобы ощутить всю мощь Mylyn, вам нужно все ваши активности (как связанные с разработкой, так и непрофильные) переработать в задачи. Каждая задача содержит в себе небольшую часть всей работы, которая будет иметь конечный результат. Разумеется, вначале с формулировкой задач будут проблемы («Написать приложение» явно не лучший вариант, так как неясно, каким должно быть следующее действие), но со временем, придет опыт, и задачи станут более четкими («Поменять форму кнопки с квадрата на круг»). Подобное саморазвитие связано с тем, что вам самим становится проще выполнять и планировать задачи, которые сформулированы более грамотно (в принципе человек бессознательно стремится к подобному планированию деятельности). Понятное дело, что все задачи будут сформулированы по-разному, но именно наиболее четко сформулированные задачи показывают, насколько эффективен Mylyn.
Еще одно преимущество задач – они показывают, в каком состоянии находится работа. Всегда можно посмотреть, что уже сделано, а что осталось. Возможность фильтрации задач по типу поможет определить то же самое, но уже для какого-то конкретного направления. В то время как фильтрация по приоритетности показывает, как много ключевых задач было сделано. (рис. 1)
Mylyn показывает лишь то, что вам необходимо
В то время как вы находитесь в своем рабочем пространстве, Mylyn ведет запись всех ваших действий, как например редактирование файлов, классов, конкретных методов и так далее. Таким образом, каждый раз когда вы затрагиваете в ходе работы какой-то артефакт (открыв файл, отредактировав тип и так далее), Mylyn отметит данную активность, которая позволить ему организовать коллекцию все того, что вам будет интересно и необходимо. И уже в дальнейшем вы будете видеть только то, что касается сферы ваших интересов. В процессе роста количества артефактов, попадающих в эту сферу, будет меняться и их отображение, например, те классы и методы, с которыми вы работаете наиболее часто, будут выделены жирным.
Рисунок 2 показывает новую задачу, после открытия конкретного класса. Важно отметить, что в иерархическом списке (Package Explorer) показан только тот класс, который упоминается в задаче. Кроме этого, список методов (outline view) пуст, собственно, потому что еще не был затронут ни один и методов открытого класса. 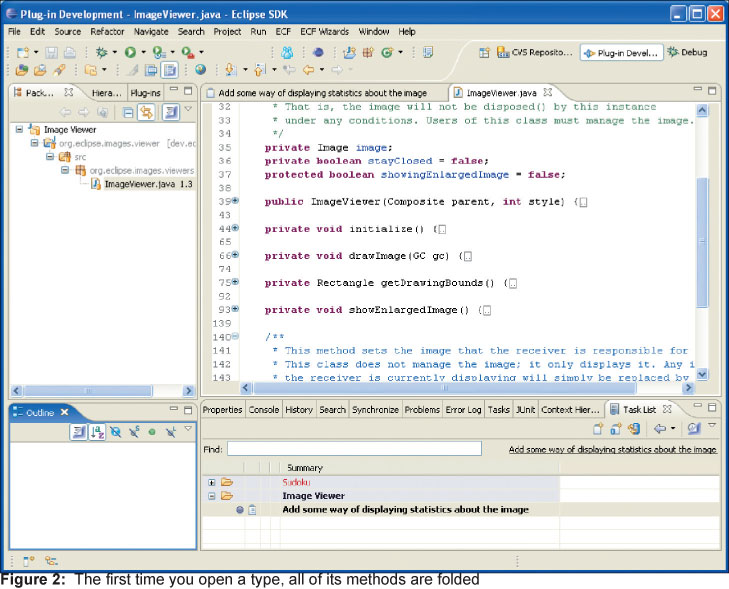
На третьем рисунке показано то же самое рабочее пространство после небольших изменений, сделанных над классом. Метод drawImage() теперь виден как в иерархическом списке, так и в списке доступных методов. Как только будут изменены другие методы, они так же попадут в область видимости. 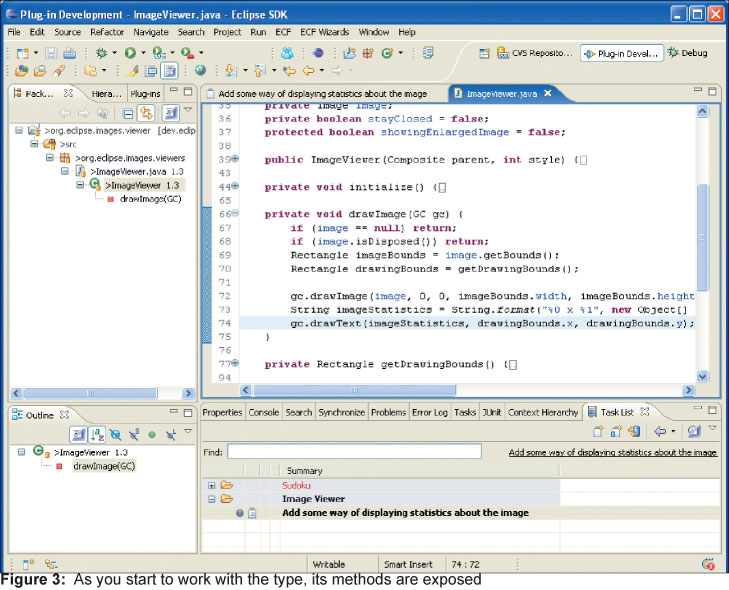
Существует и обратная реакция. Как только вы становитесь менее заинтересованным в артефакте, его выделение становится тусклым (из жирного переходит в нормальное, из нормального в серый), и постепенно артефакт пропадает из области видимости. Данный механизм основан на следующей точке зрения: если вы вносили изменение в артефакт, вы обязательно вернетесь к нему хотя бы еще раз. В дальнейшем, завершая задачу, вы возможно снова вернетесь к тем же артефактам, над которыми работали наиболее активно. Обратно так же верно: чем реже вы обращаетесь к артефакту, тем меньше будет необходимость в нем в будущем.
Данный режим с легкостью может быть отключен простым нажатием на кнопку «Focus on Active Task». Это сделано для того, чтобы вы могли найти артефакт, скрытый Mylyn, сделать его активным и вновь вернуться в прежний режим работы. Однако Java разработчики пользуются этим не так часто, в силу причин присущих Eclipse Java Development Tools (JDT), которые с легкостью позволяют просматривать родственные связи. Возможно так же отложить текущую задачу, с целью поработать над другими артефактами, или, например, другой задачей, и вернутся к первой.
Mylyn помнит,(что вы делали прошлым летом — прим. перевод.) что вы делали, пока переключались между задачами.
На следующих двух картинках можно видеть, как выглядит рабочее пространство во время работы над багами Eclipse: 138600 и 164658. Разница видна невооруженным глазом. Таким образом, мы подошли к еще одной важной особенности Mylyn: сохранение конкретного рабочего контекста для конкретной задачи. 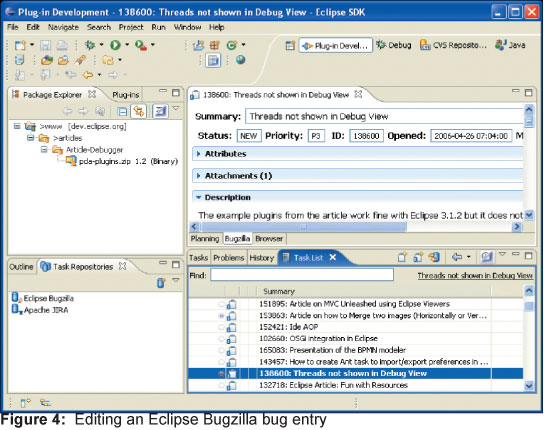
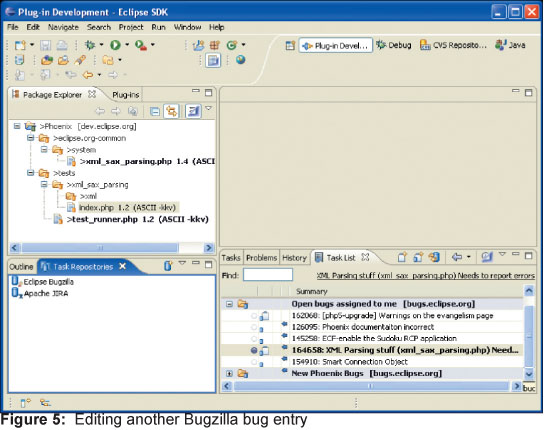
Таким образом, переключаясь между задачами, вы будете видеть только те артефакты, которые касаются только этой задачей. Важно, что только одна задача может иметь статус активной, но никто не мешает переключаться между задачами. Задачу можно сделать активной массой способов: через выпадающее меню в редакторе задач, с помощью работы с записью в меню «Navigate» или нажатием на первую колонку строке, где описана данная задача. Чтобы все было совсем просто, вы можете переключаться между задачами используя выпадающее меню, появляющееся при нажатии на заголовок вкладки “Task List”, как показано на рисунке 6. 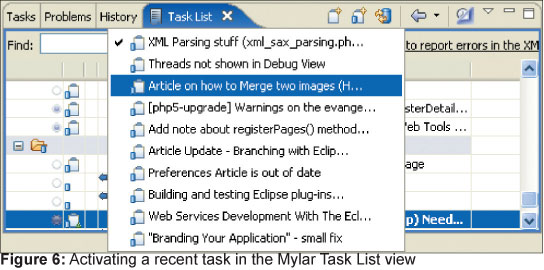
Название текущей активной задачи видно в верхней части вкладки “Task List”, а так же выделено жирным в общем списке задач.
Управляя контекстом для каждой задачи, Mylyn позволяет разработчику сфокусировать все свое внимание на хорошо сформулированной задаче и потратить как можно меньше времени, для переключения между этими задачами. Другими словами: как только вы переключились на другую задачу, вы видите тот материал, с которым надо работать. И никаких лишних временных затрат.
Mylyn может подцепляться к системам управления
На сайте Mylyn помимо всего прочего можно найти плагины для интеграции с Bugzilla, JIRA, и Trac. Кроме того, есть возможности интегрировать Mylyn с XPlannerи другими подобными сервисами. Такой функционал позволяет управлять задачами вне сред разработки, а также видеть их другим разработчикам.
Например на рисунке 7 можно видеть список задач, полученных из различных систем. Наприме, пункт «Open Harmony Bugs» позволяет подсоединиться к JIRA, используемой командой ApacheHarmony. Другие пункты меню получают позволяют видеть задачи, получаемые из EclipseBugzilla. 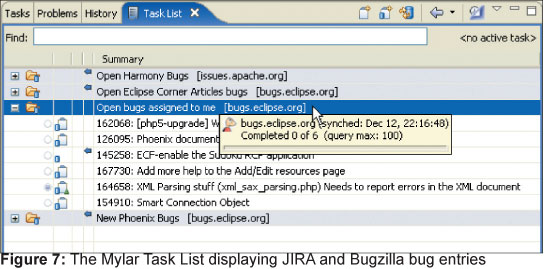
Добавление задач в свой список сводится к отправке запроса на сервер. Он возвращает ваши задачи, после чего вы можете начать работу над ними. Существует и поддержка режима работы offline; все изменения, сделанные в нем, отправятся на сервер после следующей синхронизации. Создание запросов операции более чем простая и легко выполняется с помощью диалогов, как например это показано на рисунке 8. 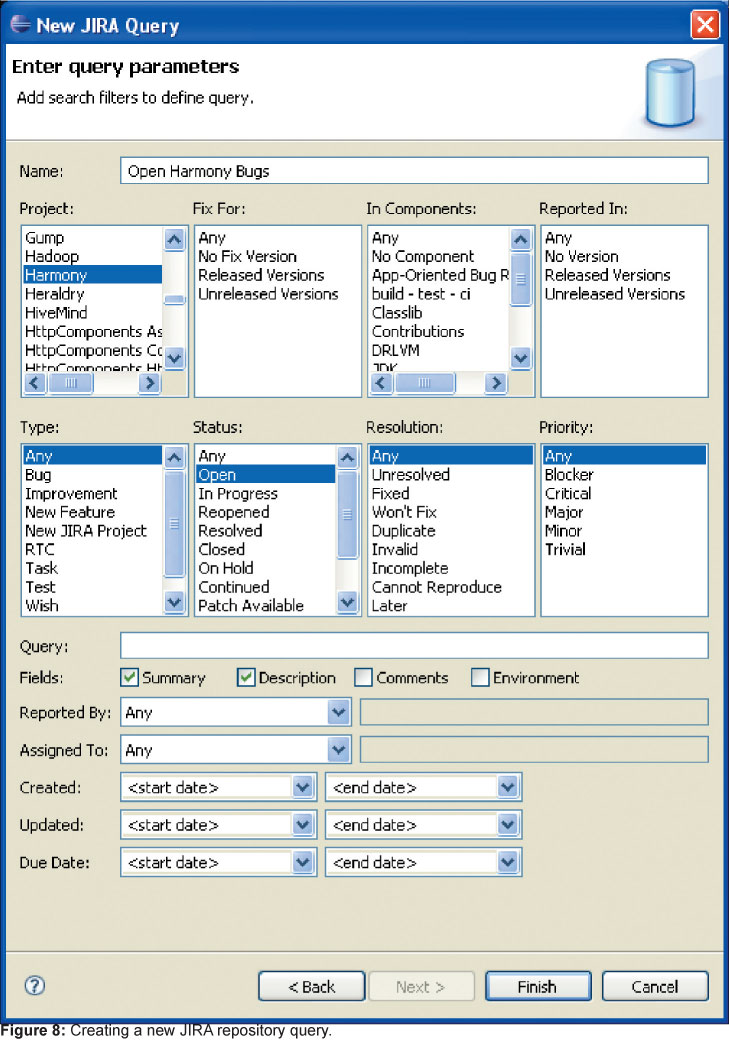
Задачи, полученные из репозитория, регулярно автоматически обновляются. Те задачи, которые были изменены, помечаются в общем списке, что сразу делает их заметным. Mylyn позволяет добавлять к задачам дополнительную информацию, включая информацию, касающуюся времени (например когда вы начнете работать над задачей), как долго вы будете над ней работать и насколько она выполнена. Так же можно выставлять длительность работы над задачей.
Существует так же возможность присоединения рабочего контекста (см. рис 9), что позволяет заархивировать рабочий контекст задачи и отправить его как дополнительную информацию на сервер. Контекст содержит информацию обо всех артефактах, с которыми вы поработали. Помимо того, что все могут видеть область вашей работы, они так же могут расширить и свой рабочий контекст вашими артефактами. В последующем вы можете работать совместно над одними и тем же контекстом. 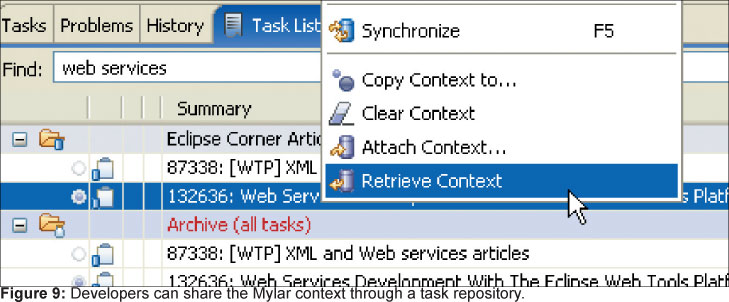
Создание дополнительных коннекторов для репозиториев задач возможно благодаря открытому API. Что касается коннекторов к другим источникам задача, включающим в себя веб-сервисы, базы данных и корпоративные программы управления задачами, то их создание так же возможно, что делает Mylyn единым средством для работы над задачами.
Mylyn имеет продуманный Look And Feel
Mylyn очень качественно интегрирован в интерфейс Eclipse. Разработчики Mylyn следовали правилу «Лучше меньше да лучше»и на выходе получили интуитивно понятный и достаточно мощный по возможностям дизайн, который при этом не является перегруженным. Mylyn можно найти повсюду, однако он нигде не кричит о своем присутствии. Большинство вкладок (включая Navigator, Package Explorer и Outline) содержат в себе функционал от Mylyn, но при этом их принцип работы остается прежним, Поэтому чтобы привыкнуть к Mylyn требуется совсем немного времени. Вместе с этим появились и нововведения (как например временное раскрытие спрятанных артефактов кнопкой Alt), но это служит больше для удобства. Продолжая эту стратегию, пункты меню, связанные с Mylyn просто добавились в список уже существующих, но при этом не внесли ничего нового.
Mylyn хорошо смотрится и при этом предсказуемо работает. Например, ненавязчивое мигание всплывающего окна в нижней правой части экрана, уведомляет вас об изменения, сделанных на сервере над задачей.
Таким образом, Mylyn –это изящное, но при этом мощное средство работы, понятное для пользователя.
Для любой предложенной задачи, Mylyn предоставляет именно те артефакты, которые почти наверняка понадобятся в будущем. Mylyn уверено отталкивает сложившиеся представления об интегрированных средах разработки: вместо того, чтобы подбирать инструменты для решения проблемы, следует распределить проблемы по имеющимся инструментам. Возможно, это не совсем очевидно, но тем не менее это так важна. Mylyn интегрируется с остальными инструментами первой необходимости, и делает разработку более эффективной и продуктивной, чем изначально позволяет среда.
Для того, чтобы осознать потенциал Mylyn, вам нужно научиться правильно формулировать свои задачи. Если задача слишком широкая, Mylyn не будет столь эффективен (в основном потому, что количество просматриваемых артефактов будет слишком велико, и мы приходим к тому, с чего начинали).
Mylyn/User Guide
Contents
Task List
At the top of the Task List, you will find the following buttons and features:
Finding Tasks
The task list can be filtered by providing a phrase to match against the task summary. The phrase must appear in the summary of a task for the task to be visible when a filter is applied. The task list filter operates by searching on a locally-maintained index of the tasks in your task list. (In rare cases, it may be necessary to manually refresh the search index by selecting «Refresh Search Index» from the task list menu.)
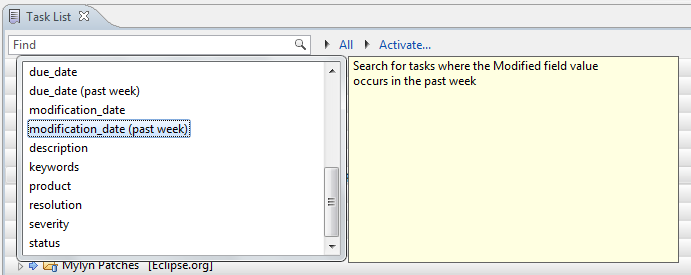
Available Fields
Available fields can be found by using content assist in the search field. The following fields are available for search with most repositories:
content match against any of summary, description, comments and other long text fields summary the task summary description match against the task description person match against any person field, such as reporter, assignee, watcher, etc. task_key match against the task or bug id attachment match against attachment names assignee match against the assignee of the task reporter match against the reporter of the task product match against the product of the task component match against the component of the task creation_date match against the date when the task was created completion_date match against the date when the task was completed due_date match against the date when the task is due modification_date match against the date when the task was last modified status match against the status resolution match against the resolution severity match against the severity
Some fields listed above may not be available depending on the repository and connector.
Search Operators
The Task List provides logical operators. For example, NPE AND Display. Note that unlike other search phrases, search operators are case-sensitive; otherwise, the words are treated as part of the search phrase.
AND Searches for tasks that contain both words. OR Searches for tasks that contain at least one word.
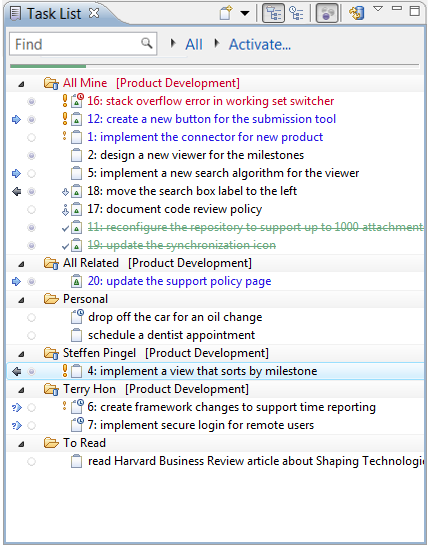
Task List Presentation
The task list supports several ways to present tasks. You can toggle between the following modes by using the «Task Presentation» button in the toolbar.
In either presentation, you can toggle the «Focus on Workweek» button. In this mode, only the following tasks will be visible:
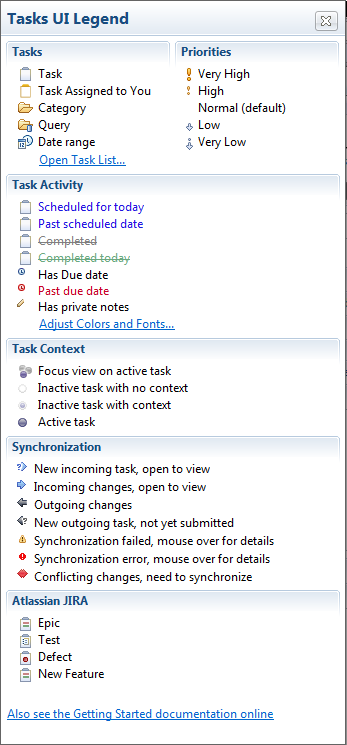
Icon Legend and Color Coding
See the legend below to interpret the icons and color coding in the task list. You can view this legend by selecting «Show UI Legend» from the menu that appears when you click the white down arrow next to the minimize button in the top right corner of the Task List view.
Creating New Tasks
You can create new tasks by clicking on the «New Task» button in the Task List’s toolbar. This will open the «New Task» dialog and prompt you to select a repository. There are two main types of tasks, local tasks and repository tasks.
Local Tasks
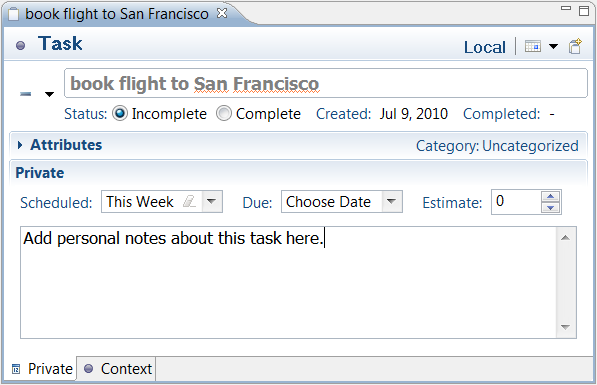
Use local tasks if you do not have a shared task repository or if you would like to create a private, personal task that is local to your workspace. To create a local task, select Local Task and «Finish» from the New Task dialog.
You can then provide the following details about the task.
Repository Tasks
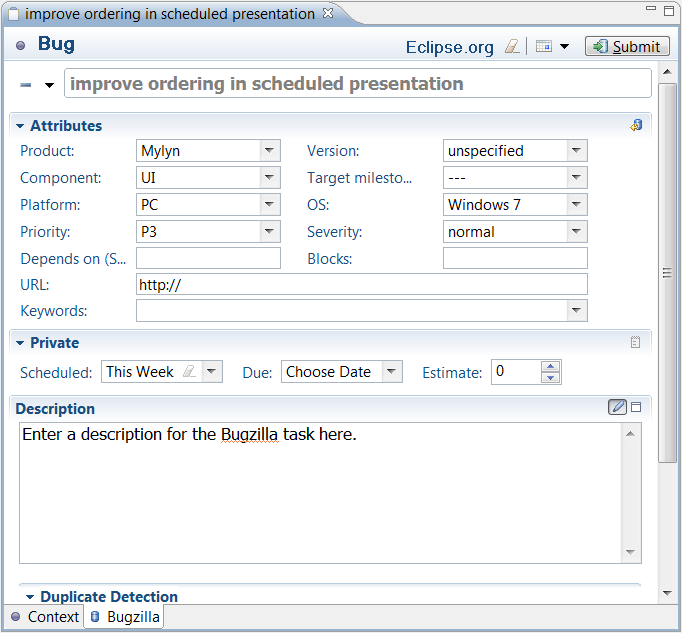
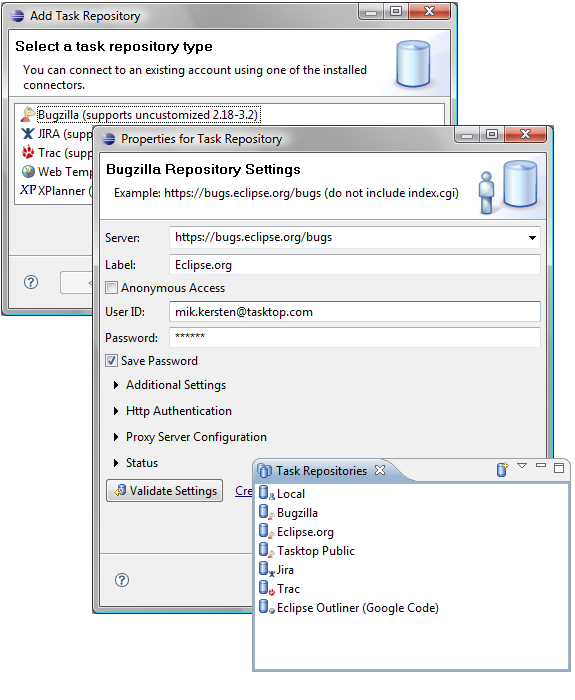
Create a new repository task when you would like to share information about the task with your team using a task repository such as Bugzilla or Trac. To create a new repository task, click on the «New Task» button in the Task List’s toolbar. You can then select the repository where you would like to create a task. If you don’t see your team’s task repository, you will need to configure it in the task repositories view. Once you have selected a repository, click «Next». If you are connecting to a Bugzilla repository, select a «Product» as a top-level category for your task and click «Finish».
A new task editor will appear. If you are using Bugzilla, you can enter the following information:
When finished, click «Submit» to add your new task to your team’s shared task repository.
Creating new Queries
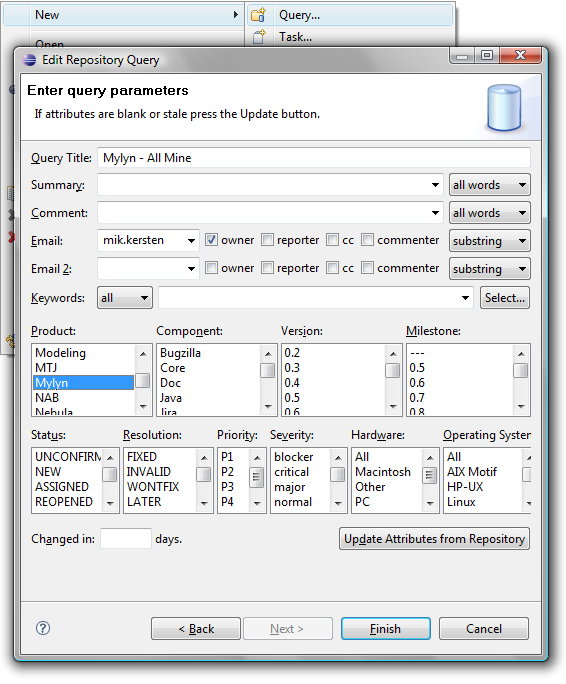
Once you have configured your team’s task repository, you can use Queries to add tasks to your task list.
If you are using the Bugzilla connector, you can specify the following parameters by default. The parameters for most other connectors will be similar.
Scheduling
Two kinds of dates for scheduling are provided.
Synchronization
Repository tasks and queries are synchronized to reflect the latest changes on the server. Tasks are synchronized the following ways:
Disconnected Mode
A task repository can be put into Disconnected mode via the right-click menu in the Task Repositories view. This can be useful if the task repository is not currently in use (e.g. you are no longer engaged with the project, or the repository is no longer available). The offline support will ensure that you can still access tasks that you have worked with via their offline copies, and the Disconnected mode will ensure that synchronization warnings do not appear. Note that it is not necessary to turn off synchronization or work in Disconnected Mode when working offline.
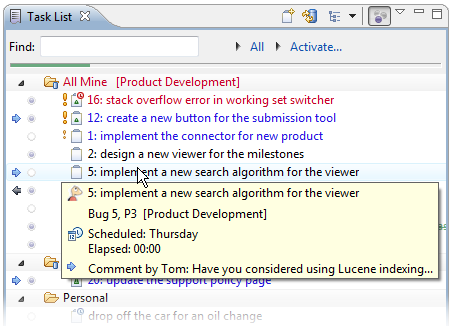
Incoming Changes
A blue arrow to the left of a task indicates that the task has changed in the shared repository. Double-click the task to view it in the task editor. Changes to the task will be highlighted in blue.
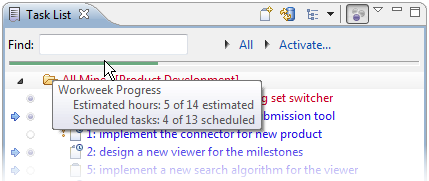
To quickly review the differences since the task was last read, hover over the task in the Task List to view a summary in a tooltip. You can also press F4 to display a tooltip. You may also wish to view the task list in «Focus on Workweek» mode, which will filter out tasks without incoming changes that are not scheduled or due this week. You can toggle «Focus on Workweek» using a button in the Task List’s toolbar.
Reviewing Tasks
The task list has been carefully designed to support quickly reviewing tasks. Task reviewing is best done by configuring a query to show the tasks that you want to review. Once the tasks are displayed in the Task List they can be reviewed one at a time by scrolling through them using the keyboard up/down arrows. The task tooltip should provide enough detail to do a review and will display information relevant to the currently selected task.
To edit the selected task press the enter key, use Ctrl+Enter to open the task in the background. To quickly jump to the next unread task hold down the Alt-key when pressing up or down. To mark a task as read while navigating use Alt+shift+up/down. When reviewing tasks in this way, it is best to avoid mouse-based and gesture-based scrolling.
Task Progress Indicators
Weekly progress
When in Focus on Workweek mode (right-most toolbar button), the Task List will show a progress bar that indicates progress on the tasks scheduled for the current week. Each task that is scheduled for the week but not yet completed adds to the bar. A task completed by you adds to the green progress in the bar. Deferring a task to a future week will also add to the apparent progress because it will remove the task from the current week. Mousing over the bar will indicate details about your progress, such as the number of tasks and hours completed. To avoid the need for manual estimation by default every task is estimated for 1 hour, but if you have longer or shorter running tasks that week you can adjust the estimate in the task editor’s Planning page to ensure that the progress bar is accurate.
Note that when in Focus on Workweek mode the Task List will show each of the tasks scheduled for this week. However, overdue tasks and those with incoming changes will also show, making the number of tasks visible not be a reliable indicator of progress on the tasks planned for the week.
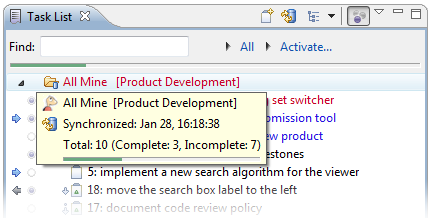
Category Progress
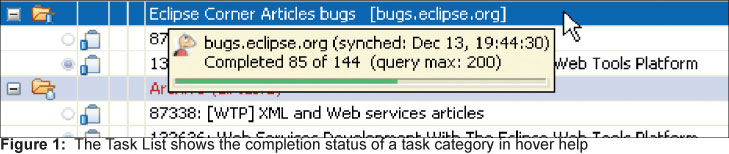
You can hover over categories in the task list to display a tooltip that displays a summary of complete and incomplete tasks.
Task List Settings and Operations
Click the small white arrow in the top right of the Task List view to access the following settings:
Right-clicking in the task list provides access to the following operations
Task Repositories
Use the Task Repositories view to configure Mylyn to connect to your team’s shared task repository (bug or issue tracker):
Task Editor
The task editor allows you to view and edit the tasks in your task list. Double-click on a task in your task list to open the editor. The features of the task editor will vary depending on whether it is a local task or a shared repository task. For shared repository tasks, there are some differences depending on the type of repository (and corresponding connector) that you are using (link: connectors).
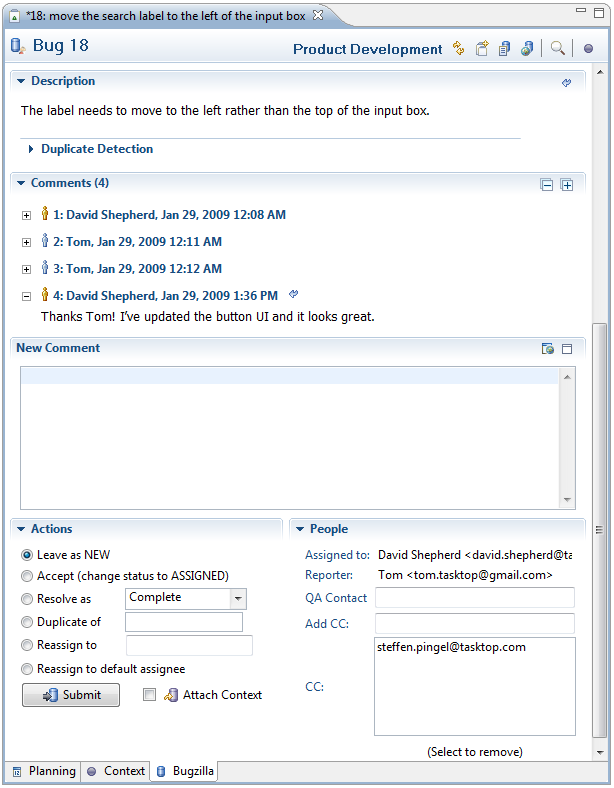
Repository Task Details
In this section, we describe the task editor for shared bugs in a Bugzilla repository. Task editors for other repository types such as Trac offer similar functionality.
Editor toolbar buttons
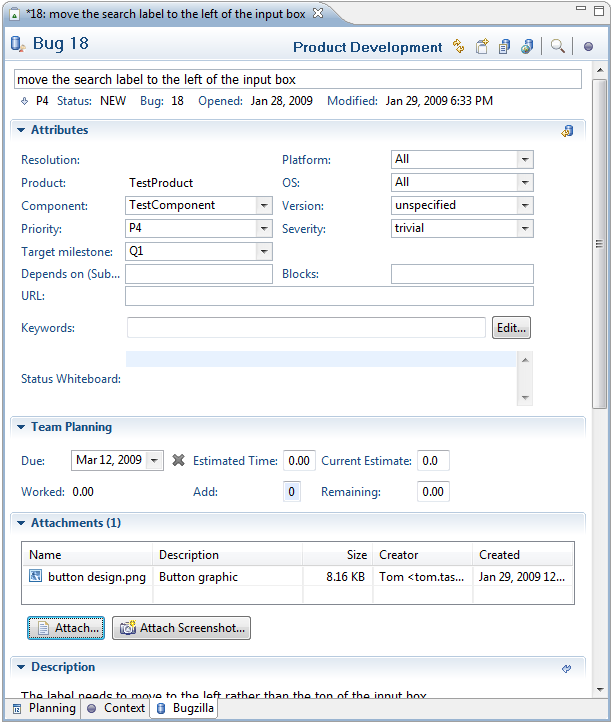
Attributes Use the Attributes section to add or update structured information about the task.
Team Planning The Team Planning section contains time-related information about the task that will be shared with your team. You can use the Due field to set a due date for your task. On the due date, the task will appear in red in your task list.
Attachments You can attach a file to this task so that a copy will be uploaded to your task repository and become available to anyone who can access the task.
Duplicate Detection When submitting bug reports, you can avoid duplicates by clicking the «Search» button. This will search the repository for a stack trace that matches a stack trace in the task’s Description field. The results of the duplicate detection show up in the Search view. If a match is found, you can open it and comment instead of creating a new bug report.
Comments Use this section to add new comments about the task and view all previous comments. Comments you have read previously are folded. You can expand and re-read individual comments or click the «+» at the top right to expand all comments.
Actions Use this section to change the task’s status or reassign the task to another person.
People This section shows the people who are collaborating on the task.
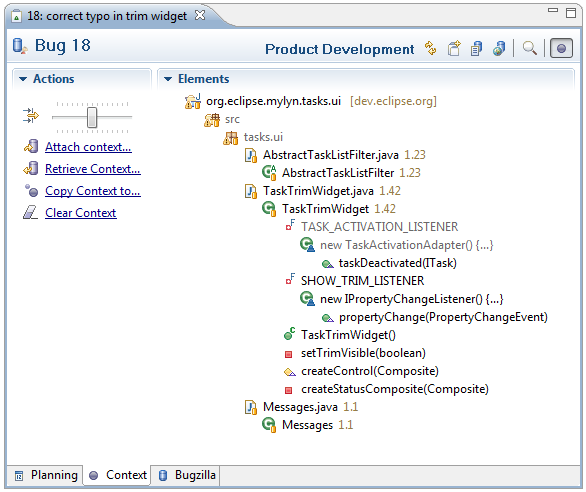
Context
The context tab allows you to manage the context of resources associated with the task. You can view the context tab by selecting it in the lower left of the editor window.
Elements
This section lists the resources that are part of the task’s context. Because the number of elements may be large, you can adjust the level of detail using the slider at the top of the Actions section. Sliding the control all the way to the left will show you all elements in your task context. As you slide to the right, only the elements with a high level of interest will be displayed. You can manually remove elements from your task context by right-clicking and selecting «Remove From Context». You may choose to view all elements and prune irrelevant items in this way before attaching the context to the task so that others can download it.
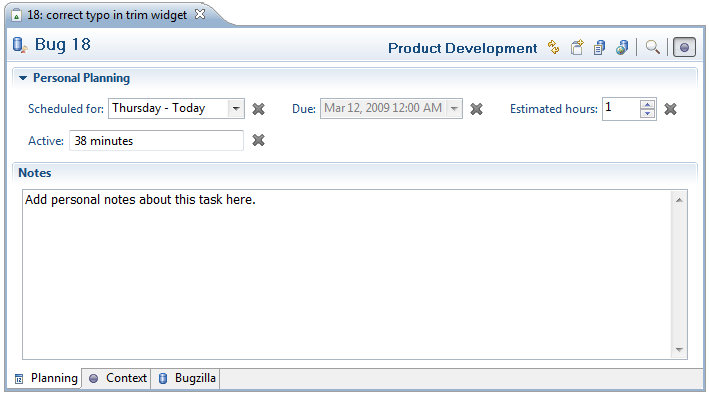
Planning
Use the planning tab to access local information about the task that is private to your workspace. You can view the planning tab by selecting it in the lower left of the editor window. This tab contains a large area where you can enter personal notes about the task. See the local task section for more information about fields in the Personal Planning section.
Task-Focused Interface
The task-focused interface is oriented around tasks and offers several ways to focus the interface on only what is relevant for the currently active task.
Focusing Navigator Views
You can focus navigator views (e.g. Package Explorer, Project Explorer, Navigator) by toggling the «Focus on Active Task» button in the toolbar. When focused, the view will show only the resources that are «interesting» for the currently active task.
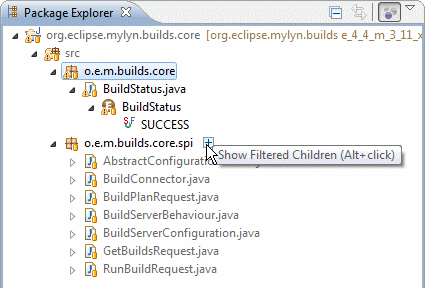
Alt+Click Navigation / Show Filtered Children
To navigate to a new resource that is not a part of the active task’s context, you can toggle «Focus on Active Task» off, browse to the resource, and then click «Focus on Active Task» again to see only relevant resources. A more efficient way to add new resources is to use Alt+Click navigation (clicking the mouse while holding the Alt key) or click the [+] icon that appears to the right of a tree node when the mouse hovers over it.
When a view is in Focused mode, you can click the [+] icon to the right of a node, or Alt+Click the node, to temporarily show all of its children.
Focusing Editors
Some editors such as the Java editor support focusing. Clicking the Focus button in the toolbar will fold all declarations that are not part of the active task context.
Task-focused Ordering
When a task is active, elements that are interesting are displayed more prominently. For example, when you open the Java Open Type dialog (Ctrl+Shift+T), types that are interesting for the active task are shown first. Similarly, when you use ctrl+space to autocomplete a method name in a Java source file, methods that are in the task context are displayed at the top.
Working Set Integration
When Focus is applied to a navigator view, the working sets filter for that navigator view will be disabled. This ensures that you see all interesting elements when working on a task that spans working sets. To enforce visibility of only elements within one working set, do the following:
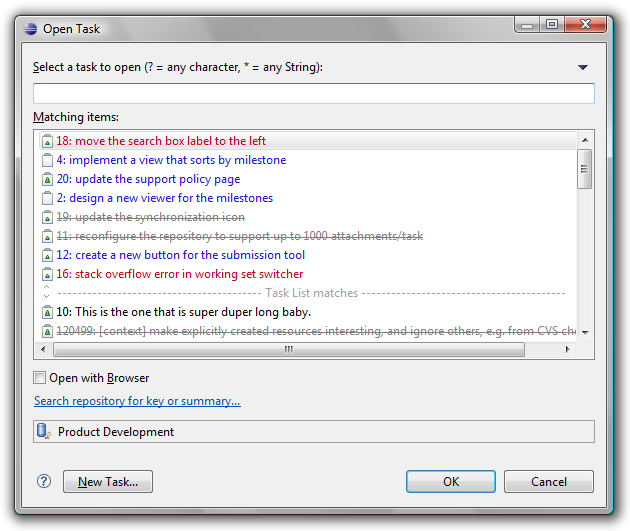
Open Task dialog
Task Hyperlinking
In the task editor, comments that include text of the form bug#123 or task#123 or bug 123 will be hyperlinked. Ctrl+clicking on this text will open the task or bug in the rich task editor.
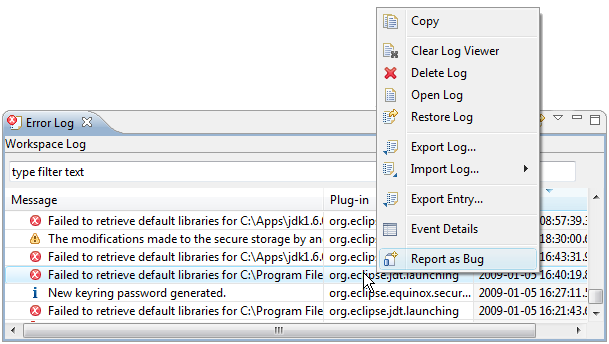
Reporting Bugs from the Error Log
Bugs can created directly from events in the Error Log view. This will create a new repository task editor with the summary and description populated with the error event’s details. If the Connector you are using does not have a rich editor, the event details will be placed into the clipboard so that you can paste them into the web-based editor that will be opened automatically.
Team Support
The task-focused interface provides several ways to improve your work flow when working with a source code repository such as CVS or Subversion. CVS support is available out-of-the-box and task-focused interface integration for Subversion is available via the Subclipse or Subversive plugins.
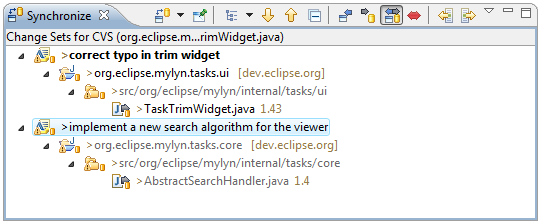
Task-focused Change Sets
When working with a source code repository, you can commit or update only the resources that are in the context of a particular task. This helps you work on several tasks concurrently and avoid polluting your workspace with changes that are not relevant to the current task.
You can use buttons in the toolbar of the Synchronize view to change modes as follows:
Right-clicking a Change Set provides access to the following operations:
Automatic Commit Messages
Note that for EGit, Task-focused Change Sets are not supported, however the commit message will be populated based on your currently active task.
Working with Patches
When applying patches, the preferred scenario is to have a task context attached to the task along with the patch. Since this is not always feasible, Mylyn provides an action in the popup menu of the Synchronize view that supports adding changed elements to the task context.
Shortcuts
Useful Eclipse shortcuts
Preferences
Tasks
Click «Advanced» to reveal the following additional settings.
Context
Use the following checkboxes to set your preferences for the task-focused interface.
Resources
Use this preference page to add or remove resources that should not be included in the context of a task. Typically, excluded files are hidden backup or lock files that are not intented to be opened directly by the user of an application.
Breakpoints
Use this preference page to enable breakpoints in context.
Task Repository Connectors
Mylyn allows you to collaborate on tasks via a shared task repository, also known as bug tracking systems. In order to collaborate, you need to have a Connector to your particular repository.
See Mylyn Extensions for a list of available connectors.
Bugzilla Connector
Trac Connector
Generic Web Templates Connector
The generic web repository connector is NOT part of the default Mylyn install. You can install it from the incubator update site. See the Mylyn download page for more details.
The web connector allow to retrieve tasks from repositories that don’t have rich connectors, but can show list of tasks on the web UI. Out of the box connector provides configuration templates for the following issue tracking systems:
Lists of issues can be extracted from existing web pages using simple parsing configuration. Configuration can be also parametrized to make it easier to customize it for a specific project.
The parameters used for configuring project properties are typically substituted into the URLs used to access the repository. Substitution and matching rules can be edited under the Advanced Configuration section on both the Repository Settings page and the Edit Query page.
See FAQ for the troubleshooting tips.
For example, consider the configuration steps for GlassFish project at java.net :
1. Create new Generic web-based repository (in the Task Repository view). GlassFish is using IssueZilla and has a preconfigured template that can be selected by server url https://glassfish.dev.java.net/issues. You can also specify all fields manually in the Advanced Configuration section. For GlassFish the following settings are required:
For the web repository that require user to login, use advanced configuration in following way. This configuration is for GForge, you might need to change it for other repositories: